From Code to Compliance: Your AppSec Risk Assessment Checklist
Last updated:13 October 2025

Running an application security risk assessment is hard. There’s the challenge of knowing where to begin, the frustration of drowning in vulnerability reports that lack context, and the constant pressure to keep up with shifting compliance demands.
Add in limited resources, sprawling third-party dependencies, and the need to keep development moving fast. No wonder so many teams feel stuck.
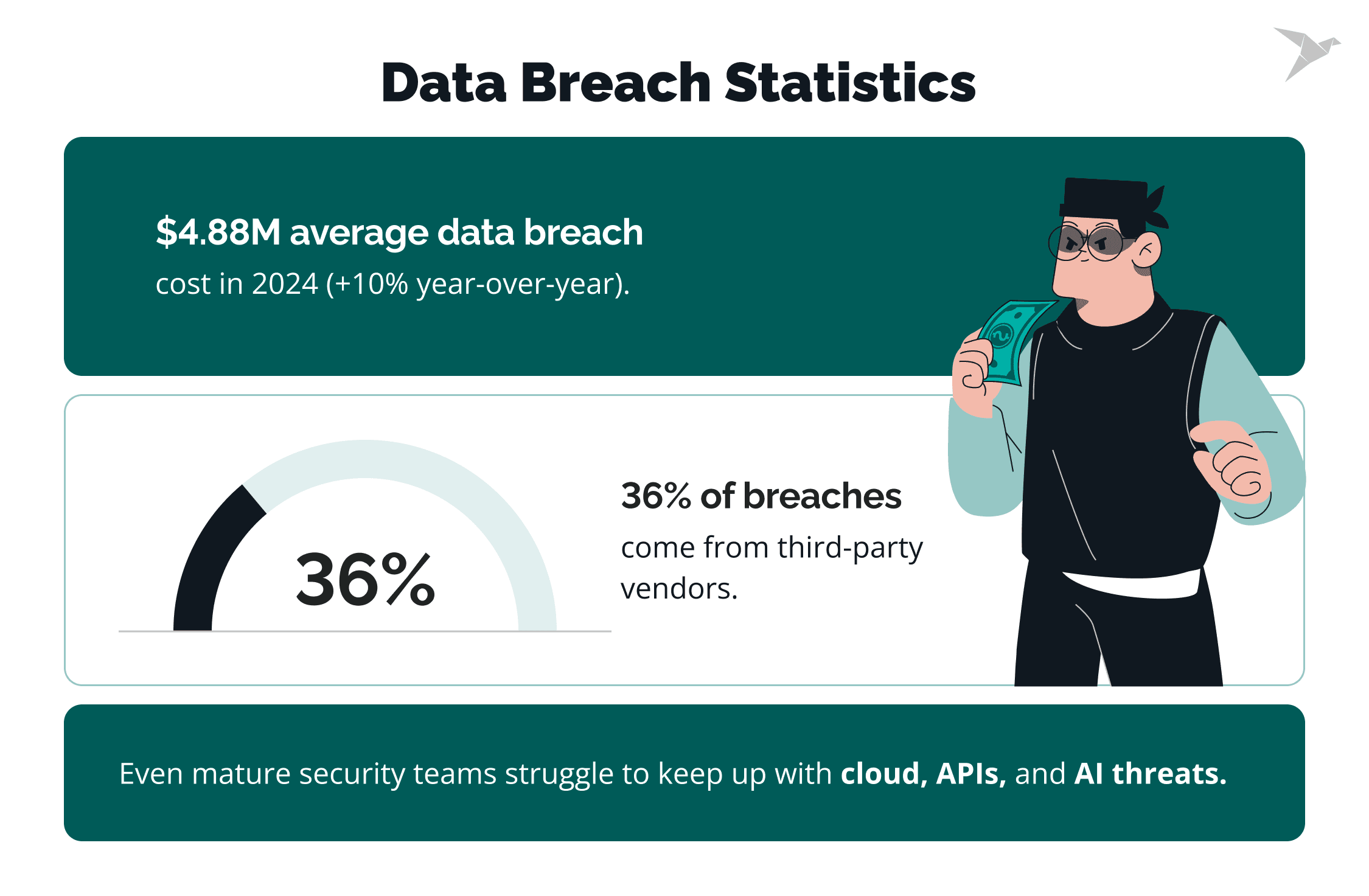
Meanwhile, the pressure keeps rising. The average cost of a data breach reached $4.88 million in 2024, a 10% jump in just one year, according to the IBM Security Report.
What’s more, nearly 36% of breaches now come from third-party vendors and partners. This proves how fragile digital supply chains have become. And with cloud-native systems, sprawling APIs, and AI-powered attack methods, even mature security programs are struggling to keep pace.
That’s why this guide focuses on the how. It gives you a clear model to follow, a practical application security risk assessment checklist you can put to work right away, and guardrails to avoid the common mistakes.
We’ll help you move from “we need better risk assessments” to “we know exactly how to assess AppSec risk, mitigate it, and stay secure.”
Key Takeaways
- AppSec risk assessments reveal blind spots across applications, APIs, and third-party systems.
- Starting assessments early in the SDLC lowers remediation costs and avoids late-stage delays.
- A mature model includes asset identification, threat modeling, vulnerability analysis, and risk prioritization.
- Cloud misconfigurations remain one of the leading causes of security incidents.
- Weak IAM policies and poor authentication are frequent entry points for attackers.
- Open-source and vendor dependencies create potential risks that can’t be ignored.
- Compliance is important, but application security assessment must go beyond audit checklists.
- Continuous monitoring and re-assessment are essential in dynamic DevSecOps environments.
- TechMagic’s Application Security as a Service helps organizations run deeper, more effective assessments. We combine testing, remediation support, and compliance alignment.
Why AppSec Risk Assessments Matter
Application security is getting harder and harder because new features, integrations, and compliance rules appear faster than most teams can keep up. Vulnerabilities multiply, and it’s never clear which ones are critical and which can wait.
Many security leaders describe it as a constant balancing act: protecting the business while keeping development moving. That’s why risk assessments matter: they separate the important from the secondary, highlight what truly puts you at risk, and give you the confidence to act on it.
Here are the key reasons in detail.

Attack surface grows in modern apps
Every new microservice, API, mobile client, or integration is another potential entry point. In complex architectures, it’s easy to lose track of all the moving parts. Application security assessments help you map them and avoid surprises.
Security needs to shift left in DevSecOps
Finding security issues late means rework, delays, and cost overruns. If assessments are delayed until QA or production, teams waste hours patching urgent flaws. Shift-left forces you to bake security into design, not retroactively.
Compliance requirements drive regular assessments
Many regulatory standards require documented risk assessment cycles and evidence of mitigation. Without a structured assessment process, you risk audit failures or fines when regulations like GDPR, PCI DSS, or HIPAA come knocking.
Breaches cost more than prevention
The average cost of a data breach reached $4.88 million in 2024, up about 10% over the prior year. That’s direct costs: lost revenue, legal, investigation, and remediation. The indirect costs, like brand damage and churn, can be far worse.
Third-party and software supply chain risks increase exposure
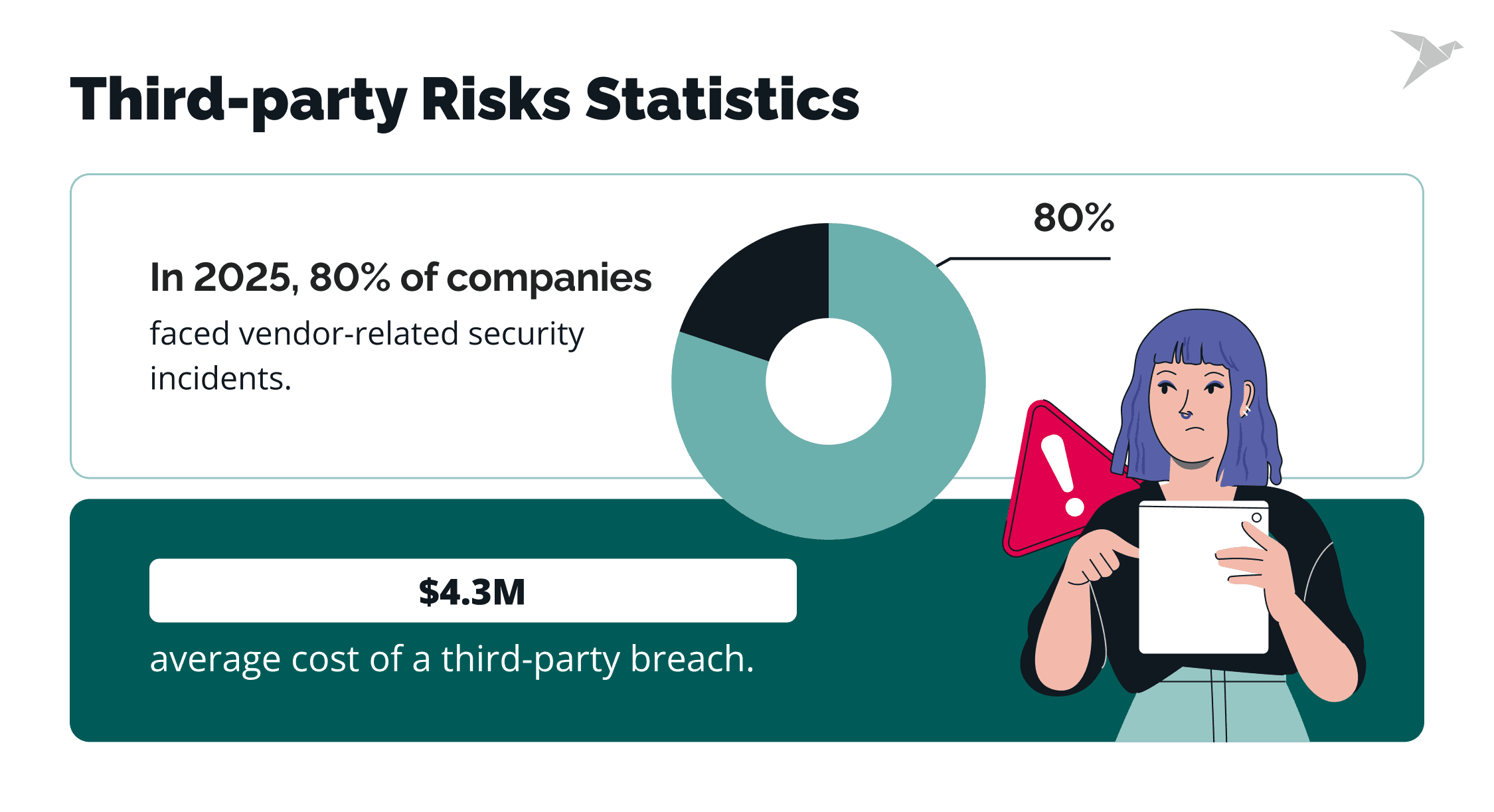
You often inherit risks from vendors you don’t control. In 2025, over 80% of organizations reported experiencing third-party vendor-related security incidents. Moreover, the average breach caused by a third party costs $4.3 million. Without assessment, these inherited application security risks can blindside you.
Cloud and hybrid systems add complexity
Misconfigurations are rampant in cloud and hybrid environments. In the Cloud Security Report by Duplo Cloud, 82% of enterprises reported security incidents linked to cloud misconfigurations. And many environments harbor at least one critical misconfiguration. Assessments help you identify vulnerabilities hidden before they’re exploited.
Customer trust depends on strong security
Trust is fragile. One breach can erode years of goodwill. If customers doubt your security, they’ll take their business elsewhere. Demonstrating structured assessments and remediations helps reassure users, partners, and stakeholders.
Security threats evolve with automation
Attackers are faster than before. Tools and scripts can probe weak endpoints at machine speed. If your risk assessment is stale or manual, you’ll fall behind. You need a process that adapts to new vectors and keeps pace.
Continuous validation is now a business must
Systems change: new features, infrastructure updates, third parties, and cloud shifts. A one-off application security assessment is obsolete within months. Ongoing validation ensures your controls still hold, and weak points don’t silently creep in.
Elements of Security Risk Assessment Model
An effective AppSec risk assessment is never improvised. It’s built on a structured model that defines what must be included every time, no matter the size of the organization or the type of application.
The following elements form the basis of a mature application security posture management and ensure consistency across teams and environments.
Asset identification as the first step
Every assessment is based on knowing what you’re protecting. That means cataloging applications, APIs, databases, cloud resources, and third-party components. Miss a single asset, and you leave an open door. Many data breaches still start with forgotten or “shadow IT” systems.
Threat modeling to understand attack scenarios
Spoiler: a list of assets is not enough. You need to know how attackers might target them. Threat modeling maps adversary tactics, potential entry points, and attack paths. This gives context: a low-level flaw in a payment API can be more dangerous than a critical bug in a low-value demo app.

Vulnerability assessment across the ecosystem
With assets and threats identified, the next task is to uncover security weaknesses. Vulnerability assessments include scanning source code, dependencies, system configurations, and infrastructure. Both automated security tools and manual review are essential here. According to Verizon’s DBIR 2024, 83% of breaches involved external actors exploiting known vulnerabilities, many of which had security patches available.
Risk analysis to measure impact and likelihood
Not every vulnerability is equal. Risk analysis quantifies both likelihood and potential impact: financial loss, data exposure, compliance penalties, or business downtime. Frameworks such as CVSS or FAIR provide a structured way to measure and explain risk in terms that link directly to business impact.
Prioritization based on business criticality
Technical severity is only one factor. A “medium” vulnerability in a system processing patient data can outweigh a “critical” issue in a testing app. Prioritization ensures resources are spent where they matter most: protecting operations, revenue, and compliance.
Mitigation strategies to reduce exposure
Mitigation means more than patching. It can include configuration hardening, adding monitoring layers, segmenting networks, or redesigning flawed architectures. The goal is to reduce the real-world exploitability of identified risks, not just close tickets.
Prevention through secure design and coding practices
The most effective risks are the ones that never reach production. Embedding security into the software development lifecycle (secure coding standards, code reviews, and security design principles) prevents vulnerabilities from being introduced in the first place. This shifts the model from reactive to proactive.
Continuous monitoring for new and evolving risks
Applications change daily. Without ongoing security monitoring, yesterday’s “clean” system can be today’s breach vector. Real-time alerts, anomaly detection, and periodic reassessments ensure the model adapts as potential threats evolve.
Automation and AI to scale risk assessments
Securing modern environments requires the right balance between automation and human expertise. While manual oversight remains essential for context and judgment, automated testing, dependency scanning, and ML-based anomaly detection increase both coverage and speed. Used well, automation helps security professionals catch more issues while reducing fatigue from repetitive tasks.
Compliance alignment to meet regulatory standards
Risk assessments are a great practice. But they’re a compliance requirement. Frameworks like ISO 27001, SOC 2, HIPAA, and PCI DSS explicitly require structured risk management. If companies integrate security standards compliance into the assessment model, they can avoid scrambling during audits and demonstrate due diligence at every stage.
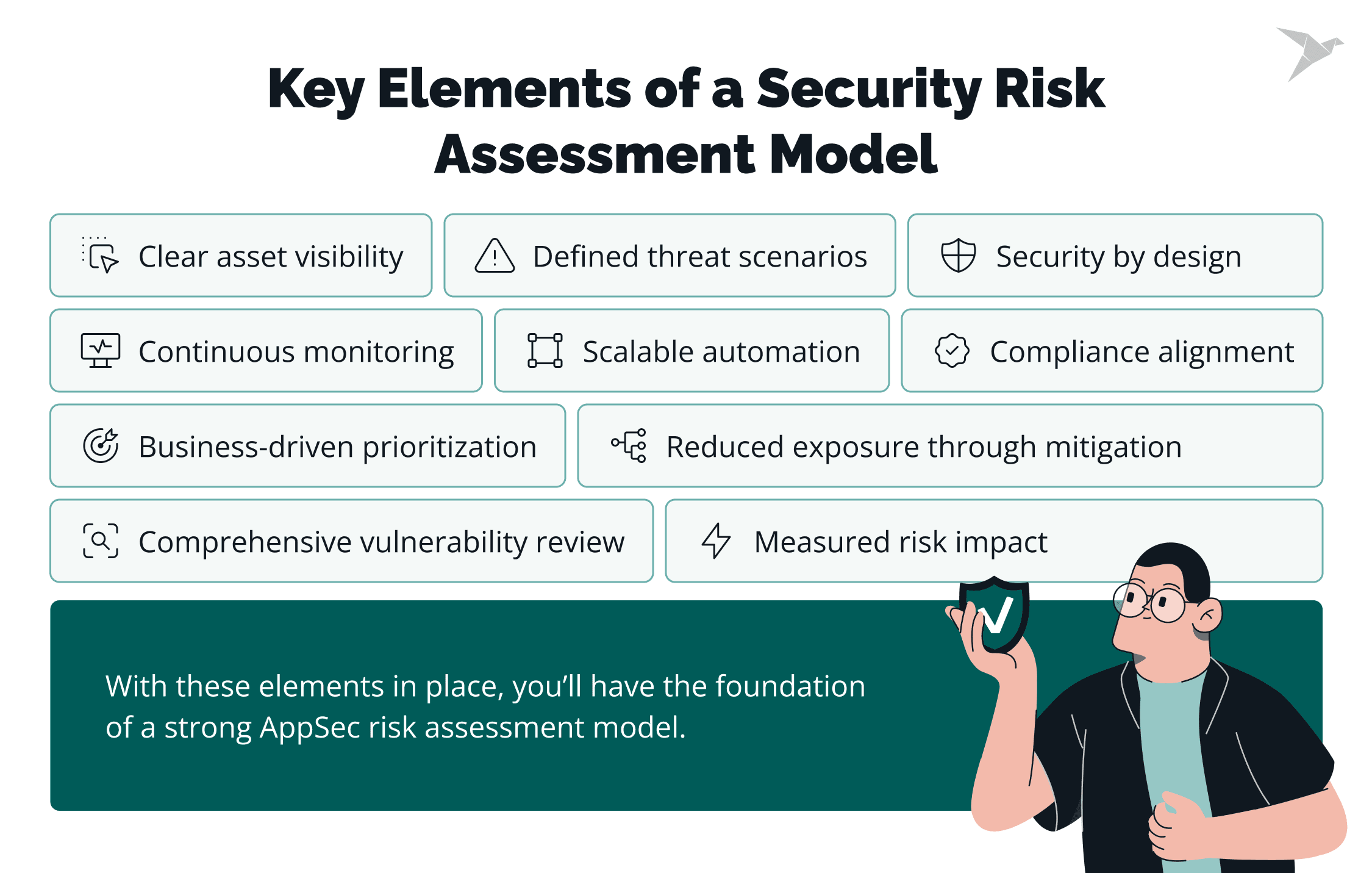
With these elements in place, you’ll have the foundation of a strong AppSec risk assessment model. In the next section, we’ll turn this structure into action: a step-by-step application security checklist you can follow to run an assessment in the real world.
Step-by-Step AppSec Risk Assessment Checklist
A strong risk assessment doesn't happen by chance. It’s the result of a disciplined process: one that balances technical depth with business priorities. Skipping steps or treating it as a box-ticking exercise often leaves organizations more exposed than before.
Below is a detailed, 16-step application assessment checklist you can rely on to run an assessment that actually improves security outcomes.
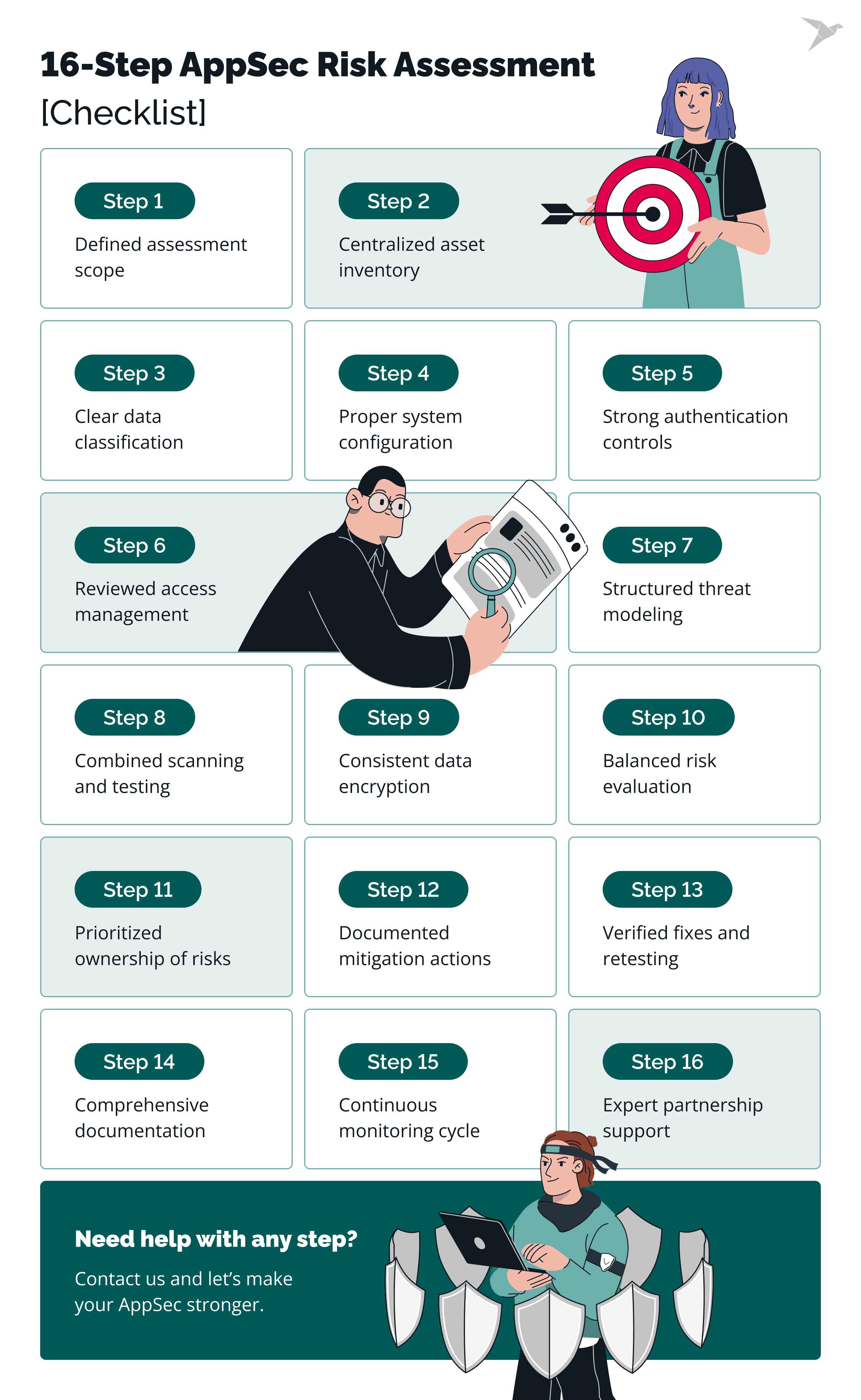
Step 1: Define the scope of the assessment
First of all, define which applications, environments, and data flows are in scope. Are you assessing one product line, a cloud platform, or your entire portfolio? Too narrow a scope leaves blind spots; too broad overwhelms resources. Mature teams document their scope in advance and revisit it regularly to stay aligned with changing business priorities.
Step 2: Create an inventory of assets and dependencies
Untracked assets are one of the most common root causes of security breaches. Build a centralized inventory of applications, APIs, libraries, cloud workloads, and third-party services. Tag assets by criticality and owner. 82% of enterprises experienced security incidents tied to unmanaged and misconfigured cloud assets in 2024. It is a reminder that what you don’t know can hurt you.
Step 3: Identify and classify sensitive data
Not all data deserves the same application security controls. Classify data into categories such as public, internal, confidential, and restricted. Highlight high-value data like financial records, customer PII, or healthcare data that carries legal exposure. Risk assessments that skip classification often misprioritize: they fix minor issues while sensitive information remains at risk.
Step 4: Ensure proper system configuration
Configuration errors are among the leading breach causes. Review firewall rules, storage permissions, IAM roles, and container settings. Automate baseline configuration checks where possible, but confirm with manual review. This step is critical because attackers actively scan the internet for exposed buckets, ports, and services.
Step 5: Revisit authentication procedures
Weak authentication is still the path of least resistance. Review password security policies, multi-factor authentication enforcement, OAuth or SAML configurations, and session management practices. According to Verizon, over 80% of hacking-related breaches involve stolen or weak credentials. Strengthening authentication is one of the highest ROI actions in any assessment.
Step 6: Review identity and access management systems
IAM controls often age poorly. Conduct role-based access control reviews, identify unused or orphaned accounts, and check privileged accounts for misuse. Pay attention to service accounts and API keys: they’re frequently over-permissioned and unmonitored. Robust access controls protect against both external compromise and insider risk.
Step 7: Perform threat modeling for critical assets
Threat modeling connects application vulnerabilities with attacker behavior. Use frameworks like STRIDE or MITRE ATT&CK to map possible attack paths. For example: if a low-severity misconfiguration enables lateral movement into your payment system, the business impact is far from “low.” Mature teams run threat modeling workshops with development teams, not just security staff, to build shared awareness.
Step 8: Run vulnerability scans and penetration testing
Combine breadth and depth. Automated vulnerability scans identify known issues across code and infrastructure. Penetration testing simulates real-world exploitation chains. Together, they surface both obvious flaws and subtle logic errors. Skipping manual testing is a common mistake. Moreover, Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST) also helps spot potential vulnerabilities while your app is running.
Step 9: Implement encryption protocols
Data encryption is only as good as its configuration. Check that TLS 1.3 is enforced, weak ciphers are disabled, and key management processes are sound. For data at rest, ensure encryption methods are applied consistently across databases, backups, and storage buckets. Many regulatory fines (like those under GDPR) stem from unencrypted sensitive data being exposed in a breach.
Step 10: Evaluate risk impact and likelihood
Quantify each vulnerability. Technical scoring systems like CVSS help, but pair them with business context: revenue impact, regulatory fines, reputational damage. For example, a medium-severity issue in an HR app may pose less risk than a lower-scoring issue in a payments platform. This hybrid approach helps executives understand what’s truly urgent.
Step 11: Prioritize risks and assign ownership
A risk assessment only matters if findings lead to action. Rank issues by severity and business importance, then assign them to accountable owners with timelines. Mature organizations track remediation in ticketing systems to ensure they don't miss anything.
Step 12: Implement mitigation and remediation actions
Remediation isn’t always straightforward. Some issues can be patched; others require redesigning workflows or adding compensating security measures and controls like WAFs or intrusion detection. Document chosen strategies and ensure they reduce the actual risk, not just the appearance of progress.
Step 13: Validate fixes and retest for assurance
Trust but verify. After fixes are applied, retest to confirm they’re effective and haven’t introduced regressions. This step is often skipped, but it’s critical: many “resolved” security vulnerabilities resurface because fixes weren’t validated.
Step 14: Document findings and align with compliance
Good documentation supports both your security team and auditors. Reports should cover scope, findings, risk ratings, mitigation actions, and timelines. They serve as proof of due diligence for compliance frameworks like ISO 27001 or SOC 2, and as a baseline for tracking improvement over time.
Step 15: Set up continuous monitoring and re-assessment
Security isn’t static. Integrate vulnerability scanning into CI/CD pipelines, set up continuous monitoring for anomalies, and schedule regular reassessments. Mature teams combine automated checks with quarterly or annual deep-dive assessments to maintain resilience against emerging threats.
Step 16: Partner with a reliable expert
Even strong internal teams face blind spots. Bringing in an external partner provides an independent perspective, access to specialized tooling, and the benefit of lessons learned across industries. This combination reduces tunnel vision and accelerates progress. Many organizations fail audits not because they lack effort, but because they lacked an objective, expert view. Consider TechMagic as a reliable partner in application security services.

In addition to the app risk assessment checklist, let us share common mistakes even experienced professionals often make!
Common Mistakes to Avoid During AppSec Risk Assessments
Even skilled security teams make errors during risk assessments. The process is complex, time-consuming, and often rushed under compliance deadlines. The result? Critical weaknesses slip through, resources get wasted, and the organization ends up with a false sense of security.
Avoiding the following common mistakes is just as important as following the right steps.
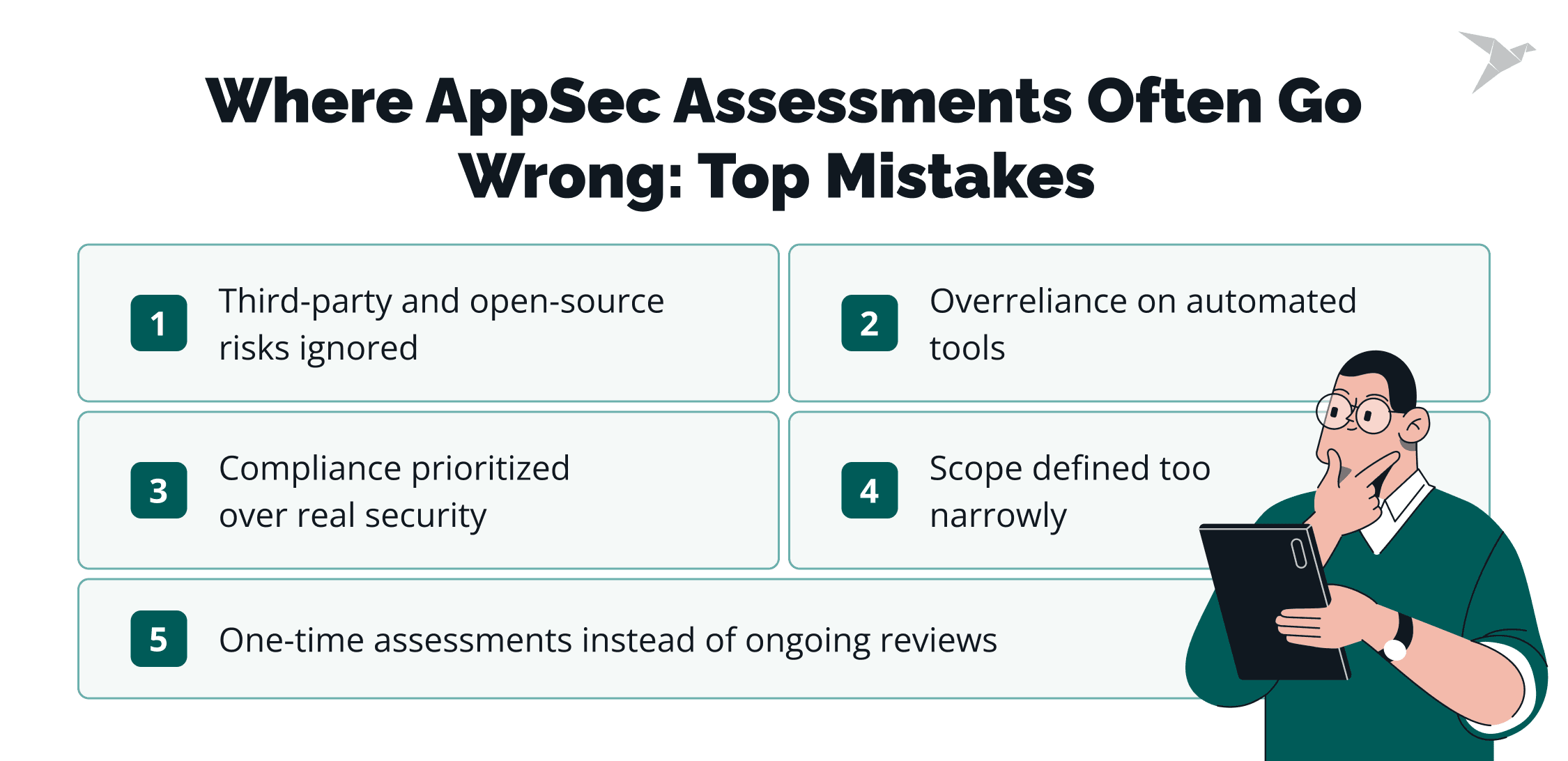
Scoping the assessment too narrowly
Defining scope too tightly (such as looking only at production apps and ignoring staging or shadow systems) creates dangerous blind spots. Attackers don’t respect your scope. In many breaches, forgotten APIs or outdated development servers were the actual entry points.
Overlooking third-party and open-source dependencies
Modern apps depend heavily on external libraries and vendor services. If these aren’t assessed, you inherit associated risks without realizing it. A 2024 Synopsys study found that 84% of codebases contained at least one known open-source vulnerability. What’s more, 49% include components with no development activity over the past two years, which means those application components are unlikely to receive patches.
Relying only on automated tools without human validation
Scanners are necessary but not sufficient. They flag known CVEs but can’t catch logic flaws, insecure workflows, or chained exploits. Manual validation and penetration testing are the only way to confirm if a vulnerability is exploitable in your environment.
Treating assessments as one-time exercises
Running a risk assessment once a year is no longer enough. Cloud-native apps and CI/CD pipelines mean systems change weekly or daily. A point-in-time application security assessment is obsolete almost immediately. Continuous validation and periodic reassessments are now the foundation.
Focusing only on compliance instead of real security
Compliance frameworks set a basis, but attackers don’t care whether you passed an audit. Over-prioritizing paperwork over actual risk leaves dangerous exposures unaddressed. A mature program treats compliance as an outcome of good security, not the goal itself.
Secure Your Applications with Confidence
Risk assessments are complex. Even the most experienced teams struggle with limited time, fast-moving codebases, and the pressure of staying audit-ready. That’s why having the right partner is vital.
At TechMagic, we help organizations run risk assessments that go deeper than just a theoretical application risk assessment checklist. Through our Application Security as a Service, we combine penetration testing, code reviews, vulnerability management, and compliance alignment into a continuous security program.
Our approach ensures risks aren’t just identified, but prioritized by business impact and remediated effectively.
If you’re building a new application or securing an existing one, we’ll help you uncover and mitigate risks, strengthen your defenses, and prove compliance with standards like ISO 27001, SOC 2, HIPAA, and PCI DSS.

Wrapping Up
Application security risk assessments are about clarity and control. They give you visibility into where your applications are most vulnerable, context to understand what matters most, and a structured way to close gaps before they become headlines.
The reality is that modern mobile and web applications are complex, and no team can secure them perfectly all the time. But with a strong model, a disciplined application assessment checklist, and the right support, you can reduce risk to an acceptable level and prove to customers, partners, and auditors that security is taken seriously.
Think of this process as ongoing, not one-and-done. Each application security assessment builds maturity, strengthens resilience, and moves you closer to security that keeps pace with your business.
FAQ

What is the difference between static and dynamic application security testing?
Static application security testing (SAST) analyzes source code or binaries without running the app, which is effective early in development. Dynamic application security testing (DAST) evaluates a running application. It simulates real-world attacks to find runtime flaws. Mature security programs use both to strengthen an application's security posture.
How do I prioritize identified vulnerabilities in a risk assessment?
Use a combination of technical severity (CVSS scores), business impact, and exploitability. For example, a medium CVSS issue in a payment gateway may rank higher than a critical issue in a test app. Context matters more than raw scores.
What are the key compliance requirements for AppSec risk assessments?
Frameworks like ISO 27001, SOC 2, PCI DSS, HIPAA, and GDPR all require organizations to identify, evaluate, and manage risks. Regular risk assessments and documentation of findings and remediation are essential for proving compliance.
How often should I conduct an AppSec risk assessment?
At a minimum, annually. But best practice is to reassess after major code releases, infrastructure changes, or regulatory updates. Continuous monitoring tools can fill the gaps between full assessments.


















 TechMagic Academy
TechMagic Academy