How To Build an EHR System: Steps, Benefits, and AI-Features
Last updated:11 August 2025

Did you know nearly 70% of physicians say their EHR systems slow patient care down rather than help it? This is what a survey by MPI Group found. What’s more, 1 in 3 nurses report EHRs as a key burnout factor, often citing slow load times, clunky workflows, and poor usability.
If you're building or scaling a HealthTech product, you're probably facing this reality: legacy EHRs drag your team's productivity. They stall workflows. They don't talk to labs or billing systems. They frustrate clinicians.
This guide will show you how to create an EHR and avoid those pitfalls. We'll explain how to build your own EHR system step-by-step, when to choose a custom solution, which features matter most, and how to weave in AI smartly.
At TechMagic, we know what we're talking about. We'll draw from our experience developing MHC's custom EMR platform, where the portal fits real workflows, not the other way around.
Ready to discover how to build an EHR system that's usable, scalable, and compliant?
Ideal for your team, your patients, and your mission.
If yes, let's start!
Key Takeaways
- EHRs and EMRs differ: EHRs support care coordination across providers, while EMRs are limited to one organization.
- There’s a high need for better workflows and data usability. So the global EHR market is growing rapidly.
- Custom EHR systems are better suited for unique workflows, integrations, scalability, and compliance needs.
- Building a custom EHR involves 10 thoughtful steps.
- Key features include patient portals, role-based access, lab integration, scheduling, and documentation tools.
- AI can automate documentation, optimize billing, support clinical decisions, and improve patient engagement.
- Voice tools and chatbots reduce admin burden and enhance user experience for both staff and patients.
- HIPAA compliance must be built in from day one: encryption, access control, audit logs, and regular updates.
- Medplum is a flexible, FHIR-native backend that speeds up secure and compliant EHR development.
- A well-built EHR should reduce friction, improve outcomes, and grow with your healthcare organization.
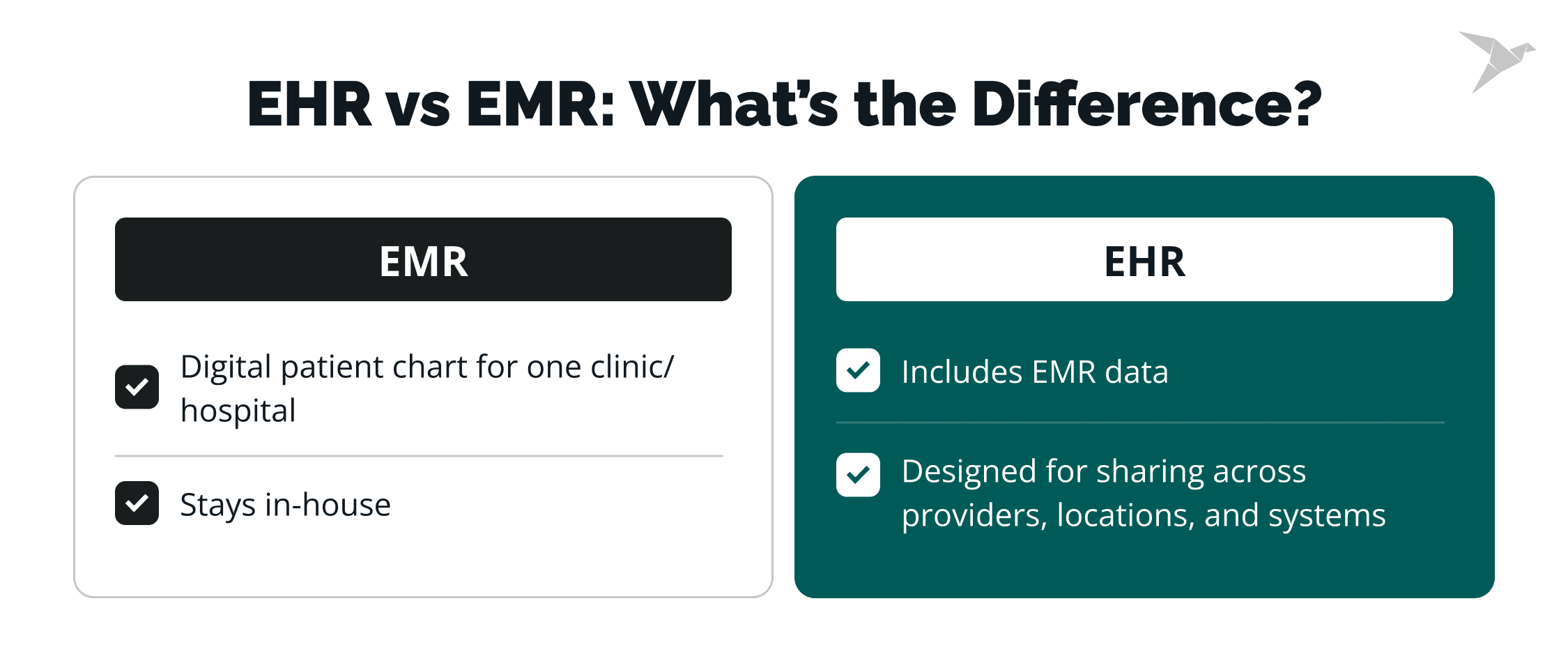
EHR and EMR System: What Is the Difference? (and Is There Any)
Yes, there is a difference. And it matters more than most people think.
An EMR (Electronic Medical Record) is the digital version of a patient’s chart used within a single healthcare organization. It includes diagnoses, treatment plans, prescriptions, and notes, but it stays in-house. Think of it as a digital filing cabinet for one clinic or hospital.
An EHR (Electronic Health Record), on the other hand, goes further. It’s built for sharing. An EHR includes all the clinical data from an EMR, but it’s designed to move with the patient across clinics, specialists, labs, and even states. It gives different providers access to a single, unified view of a patient’s care journey.
That difference opens real-world advantages:
- Better coordination between providers
- Fewer duplicate tests
- Smarter care decisions based on shared history
- A foundation for remote care, AI, and patient-facing tools
So if you’re planning a custom EHR software development process, ideally, don’t just think “how to create an EMR.” Think how to create EHR software that supports your long-term care model, partnerships, and product roadmap.
EHR Systems: A New Era for the Healthcare Industry?
No modern healthcare organization can work effectively without their own EHR software.
Not because they’re trendy. But because they solve real, growing problems.
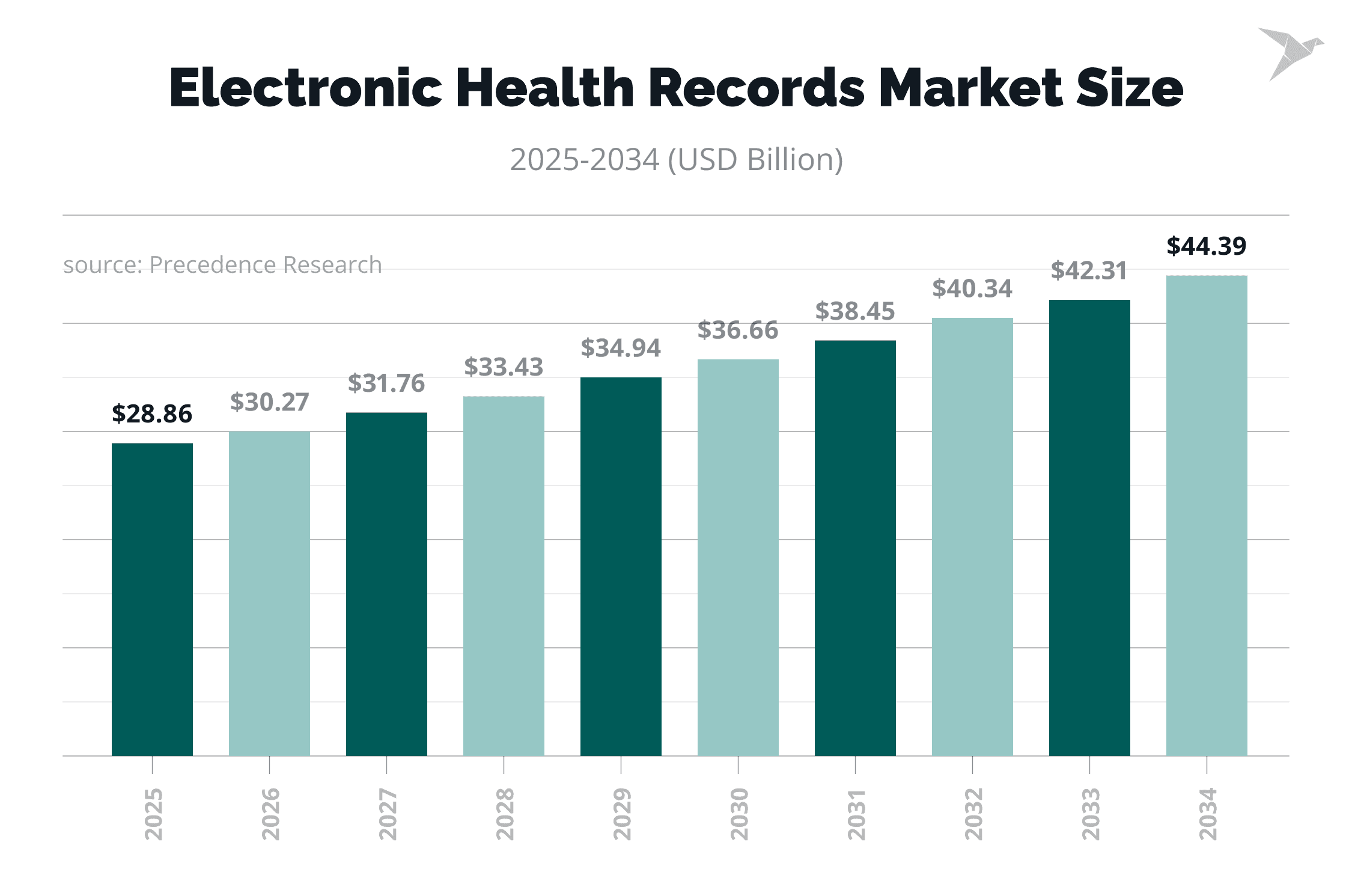
The global EHR market is projected to hit $44.39 billion by 2034, growing steadily at a 4.9% CAGR, according to Precedence Research. That growth is pretty natural as EHRs help healthcare providers do more with fewer clicks, clearer data, and smarter workflows.
Health systems and digital health startups alike are under pressure to:
- Reduce time spent on repetitive tasks
- Improve patient communication and experience
- Enable more personalized, coordinated care
- Make data usable across systems and providers
EHRs, if built right, can be the foundation for all of that. But that means moving beyond out-of-the-box software. It means building platforms that are flexible, connect easily to other tools, and actually fit how clinicians and admins work day to day.
HIPAA-compliant portal for secure medical data records and exchange

When (and Why) Custom EHR Systems Are Better Than Ready-Made Solutions?
Buying off-the-shelf can be fast.
But building the right thing? That’s where custom wins.
Not every healthcare team has the same needs. Some are rolling out new care models. Others are managing data across clinics, labs, and partners. And some just want to stop fighting their EHR and start making it work for them.
Here’s when custom EHR system development makes more sense than settling for ready-made:
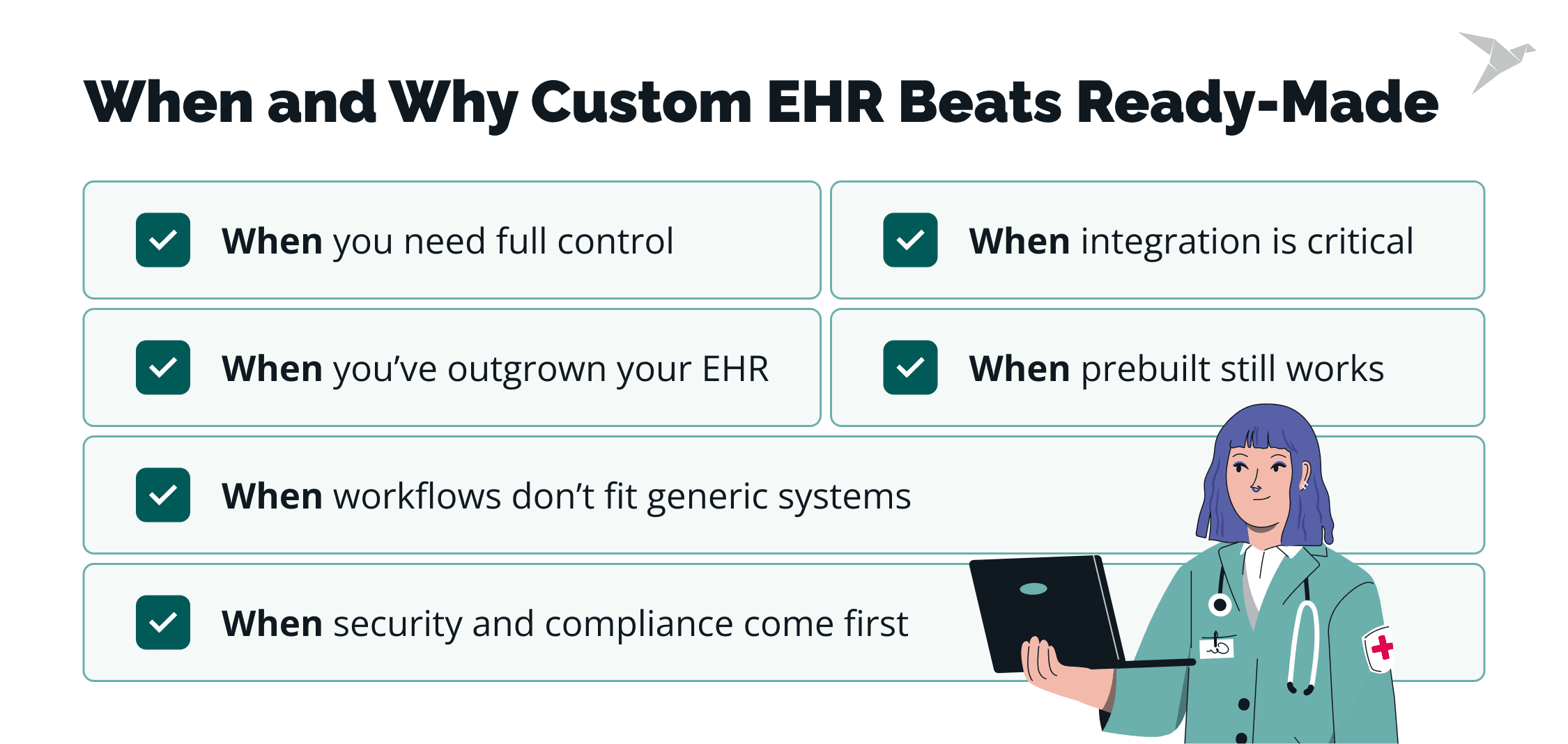
When your workflows don’t fit a generic system
Most EHR platforms force your team to adapt to their logic. That means more clicks, more frustration, and less time with patients. A custom system flips that. You build it around how your team already works, so it fits from day one.
When you want full control over features, interface, and scale
Need to add AI-based triage later? Want a simple interface for front desk staff, and a power-user dashboard for specialists? A custom EHR gives you full control over what’s built, how it looks, and how it grows.
When integration with your tech stack is non-negotiable
Third-party labs. Pharmacy systems. Insurance APIs. Legacy CRMs. If you need your tools to talk to each other, prebuilt platforms often get in the way. A custom EHR connects the dots cleanly and securely.
When security, compliance, and control are a top priority
Custom systems let you bake in HIPAA compliance, access control, and audit trails at the architecture level. You don’t have to wonder if your setup meets the standard. You'll know, because you built it that way.
When a prebuilt EHR still makes sense
If you’re a small clinic with simple needs, a limited budget, and no internal tech team, starting with a ready-made solution might be smarter for now. Just know its limits. When those limits start slowing you down, custom becomes the next step.
When your team has outgrown its current EHR
You’ll know the signs: workarounds, duplicate entries, and shadow spreadsheets. A custom EHR replaces that friction with something purpose-built. One platform that scales as you grow, not one you have to outgrow again.
How to Build an EHR System: 10 Steps to Enjoying Your Custom Solution
You're building software. But you're also building a tool that real people will use in high-stakes environments, every day. That’s why every phase needs to be thoughtful, practical, and aligned with your clinical and operational goals.
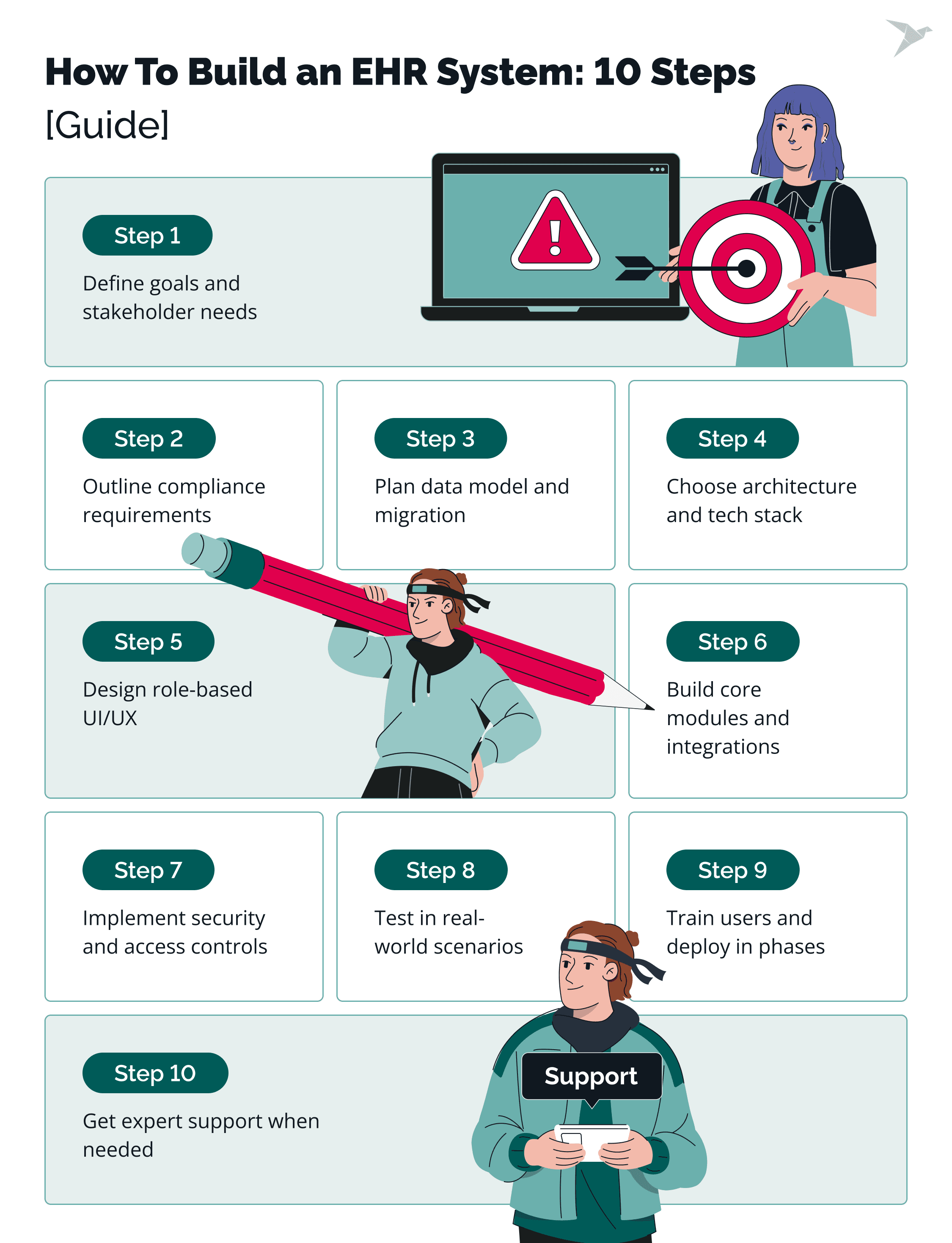
Step 1. Define your clinical goals and stakeholder needs
Start by understanding your why. What problems are you trying to solve? Are you aiming to reduce documentation time, improve care coordination, or simplify scheduling for high-volume clinics?
Talk directly to the people who will use the system:
- Clinicians (doctors, nurses, specialists)
- Admins and front-desk staff
- Compliance and billing teams
- Patients (if you’re building a portal or app)
Their pain points will shape everything from features to design.
Skipping this step leads to systems that look good on paper but fail in practice.
Step 2: Outline regulatory and compliance requirements from day one
HIPAA, HITECH, GDPR, and local data laws define how you store, transmit, and protect patient data. This step involves working with legal and compliance teams to map out:
- What data is considered PHI (protected health information)
- Who can access what, and when
- How access is tracked and logged
- What happens if there’s a breach or audit
These insights directly inform your data architecture, access controls, and backup strategies.
Step 3: Plan your data model and data migration strategy
You need to define the structure of your system’s brain: what data you’ll collect, how it’s stored, and how it moves across your platform.
Key parts of this planning stage:
- Designing data models for patients, visits, providers, medications, labs, and documents
- Deciding how structured vs. unstructured data will be handled (e.g., forms vs. clinical notes)
- Creating a safe plan to clean and migrate legacy data if you're replacing an existing system
- Ensuring FHIR or HL7 compatibility for external integrations
Get this part right and your system will stay organized and interoperable as it grows.
Step 4: Choose the right architecture and technology stack
The right technical foundation supports performance, robust security measures, and scalability. You’ll need to decide:
- Cloud vs. on-premise vs. hybrid
- Monolithic vs. modular architecture
- Front-end and back-end frameworks (e.g., React, Angular, Node.js, Java)
- Databases suited to healthcare workloads (e.g., PostgreSQL, MongoDB, DynamoDB)
This isn’t just a developer decision. It’s long-term flexibility: can your system handle AI modules, mobile access, or global expansion later? At TechMagic, we always align tech decisions with business goals from the start.
Want a head start?
Medplum is an open-source backend designed for healthcare apps. It’s FHIR-native and takes care of the heavy stuff (identity, scheduling, audit logs, security, APIs) so you don’t have to.
It’s fast, flexible, and won’t lock you in. At TechMagic, we offer custom Medplum development to help teams launch smarter.
So, choose tools that grow with you and make life easier for your devs and your users.
Step 5: Design intuitive UI/UX for every user role
A beautiful interface is meaningless if it frustrates the people using it.
Design role-based workflows so that:
- Nurses can log vitals in seconds
- Doctors can access patient histories fast
- Admins can schedule and bill without switching screens
- Patients can book, message, or view results with no training
Good UX reduces errors, boosts user adoption, and improves patient outcomes. We always prototype early, test with real users, and refine before development begins.
Step 6: Build core modules and set up third-party integrations
Start with what matters most to your care delivery model:
- Patient profiles and demographics
- Clinical documentation and note-taking
- Appointment scheduling
- E-prescriptions and medication management
- Billing and insurance claims
- Patient portal
Then connect to labs, pharmacies, wearables, and insurance systems using APIs, HL7, or FHIR. Integrations shouldn’t feel like “extras”. They're core to how your EHR works in the real world.
Step 7: Implement airtight data security and access controls
Security should never feel bolted on. It should be built into your system’s DNA. That means:
- AES encryption for data at rest and TLS for data in transit
- Role-based access control down to the field level
- Multi-factor authentication for staff logins
- Comprehensive audit trails that show who accessed what, when, and why
- Secure backups and disaster recovery protocols
This step protects both your organization and your patients. It also lays the groundwork for HIPAA, GDPR, and other regulatory compliance standards.
Step 8: Test the system extensively in real-world scenarios
Before you go live, test like your clinicians’ time and your patients’ safety depend on it.
Go beyond automated testing. Include hands-on testing by real users across every role:
- Simulate full patient journeys
- Try edge cases (like canceled appointments, billing disputes)
- Test speed under load
- Validate interoperability with external systems
- Confirm data accuracy and integrity
A well-tested system launches with fewer surprises and faster adoption.
Step 9: Train users and deploy in phases
Training is a part of successful adoption. Offer:
- In-person or virtual walkthroughs tailored to each role
- Step-by-step guides and embedded tooltips
- Support channels to handle user feedback and questions
Don’t try to switch everything on at once. Phase your rollout by location, department, or feature set. This lowers risk, builds confidence, and lets you catch any missed edge cases in a controlled way.
Step 10: Don’t go it alone – ask for help when you need it
Custom electronic health record development involves product strategy, compliance, architecture, security, design, and support. If your internal healthcare software developers don’t have capacity or experience, bring in a partner.
At TechMagic, we’ve helped healthcare teams like MHC go from idea to live platform safely, securely, and with a roadmap for what’s next. We help you think through every decision that affects your users and your growth.
Looking for expert support? Explore our EHR software development services to see how we help healthcare teams build secure, flexible systems that actually work.
We're here to assist

What Are the Necessary Features of an EHR System?
Every feature in your app should solve a real problem for real users. That’s why thoughtful EHR system development = building tools that make work easier, safer, and more connected for everyone involved.
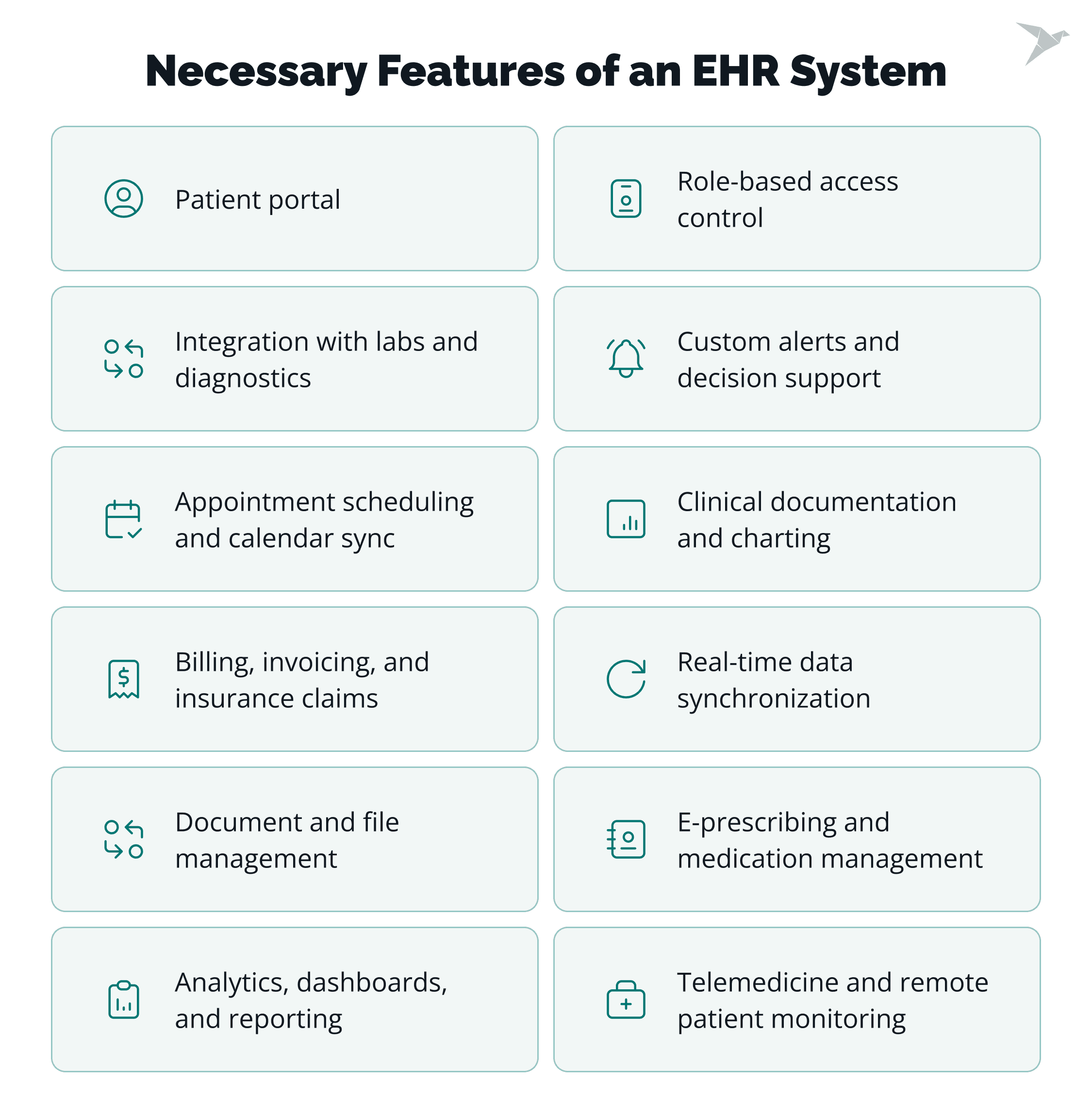
Patient portal
A well-designed patient portal gives patients direct access to their medical records, test results, prescriptions, and appointment history. But it’s more than just access. It's an engagement.
Patients can schedule visits, refill medications, message providers securely, and even view bills or make payments online. This reduces inbound calls and paperwork, improves transparency, and encourages patients to take a more active role in their care.
Role-based access control
In healthcare, not everyone should see the same data. Role-based access lets you define exactly who can view, edit, or share information based on their role. A nurse may be able to enter vitals, but not update diagnoses.
A front-desk admin can manage scheduling, but not see clinical notes. This protects patient privacy, supports HIPAA compliance, and reduces the risk of errors, especially in large teams or multi-location environments.
Integration with laboratories and diagnostics
One of the biggest time-wasters in legacy systems is the lack of lab integration. Clinicians often wait for faxes or scan PDFs just to see basic test results. With lab and diagnostic integration, test orders and results flow directly into the EHR.
Everything is time-stamped, standardized, and visible alongside the rest of the patient record. That means faster decisions, fewer missed results, and no more chasing paper.
E-prescribing and medication management
Writing and tracking prescriptions should be fast, safe, and seamless. With integrated e-prescribing, providers can look up medications, check for drug interactions, and send prescriptions directly to the patient’s preferred pharmacy without leaving the system.
When medication management is built-in, it also becomes easier to track adherence, flag potential risks, and create a complete treatment plan inside the EHR.
Appointment scheduling and calendar sync
Scheduling affects almost every part of a healthcare business. An effective EHR lets staff view provider availability in real time, book or reschedule visits without friction, and sync calendars across departments.
Patients benefit from reminders, reduced wait times, and fewer errors. Providers benefit from a clear, balanced schedule and fewer no-shows. And everyone saves time while avoiding the back-and-forth that happens in disconnected systems.
Clinical documentation and charting tools
Fast, accurate documentation is critical, but it shouldn’t slow down the visit. Your EHR should offer flexible options for note-taking: structured templates, free-text notes, auto-complete fields, or even voice-to-text.
When documentation fits naturally into the provider’s workflow, it improves chart accuracy, reduces fatigue, and keeps everyone focused on patient care instead of screens.
Billing, invoicing, and insurance claims
If billing is siloed from the clinical workflow, mistakes and delays are inevitable. A well-built EHR links clinical documentation directly to billing codes, so invoices can be created automatically based on services provided.
Insurance claims can be submitted electronically, reducing denials and speeding up reimbursements. For private medical practices, this feature can directly impact revenue cycle efficiency and cash flow.
Real-time data synchronization across departments
In multi-role healthcare teams, communication gaps can lead to missed information, double documentation, or critical delays. Real-time sync ensures that when one person updates a patient’s record, it’s instantly reflected across the system.
When it’s a diagnosis, a new lab result, or a schedule change, everyone sees the same thing at the same time. That level of visibility creates trust, saves time, and improves care coordination.
Document and file management
Beyond structured data, EHRs must also handle files: consent forms, referral letters, scanned records, or imaging reports. Document management features should allow users to upload, categorize, tag, and retrieve files without hassle.
Security and access control remain essential, but so does usability. Files should be easy to find and quick to load because in clinical settings, every second counts.
Custom alerts and clinical decision support
The best EHRs help providers stay on top of what matters without overwhelming them. Custom alerts can notify a provider if a patient is overdue for a screening, at risk for a condition, or prescribed a medication that conflicts with another.
Clinical decision support tools use logic or AI to flag issues or suggest next steps based on current data. These tools should be context-aware and configurable, so they support good decisions without interrupting care.
Telemedicine and remote patient monitoring
As more care moves online, your EHR should be ready. Built-in telemedicine lets providers run virtual visits, share screens, document in real time, and follow up in one place.
Remote monitoring adds another layer: allowing patients to send data from wearables, home testing kits, or symptom trackers. When integrated properly, these features support chronic care, behavioral health, and rural access without adding operational complexity.
Analytics, dashboards, and reporting
A modern EHR system should help you use data. Dashboards and analytics tools let you track key metrics across clinical, operational, and financial areas. That could mean spotting missed follow-ups, tracking provider workload, or monitoring billing efficiency.
The key is simplicity: visual, real-time data that’s easy to act on, without needing a full BI team.
How AI Can Be Integrated Into an EHR System
AI is the quiet helper in the background, doing the hard stuff so your team doesn’t have to. Used well, AI takes the pressure off healthcare professionals: doctors, nurses, and admin staff. It helps them focus more on people and less on paperwork, coding, or chasing lab results. And when you build a custom EHR system, you get to decide exactly where that help shows up. Here are the key use cases of AI in an EHR system:
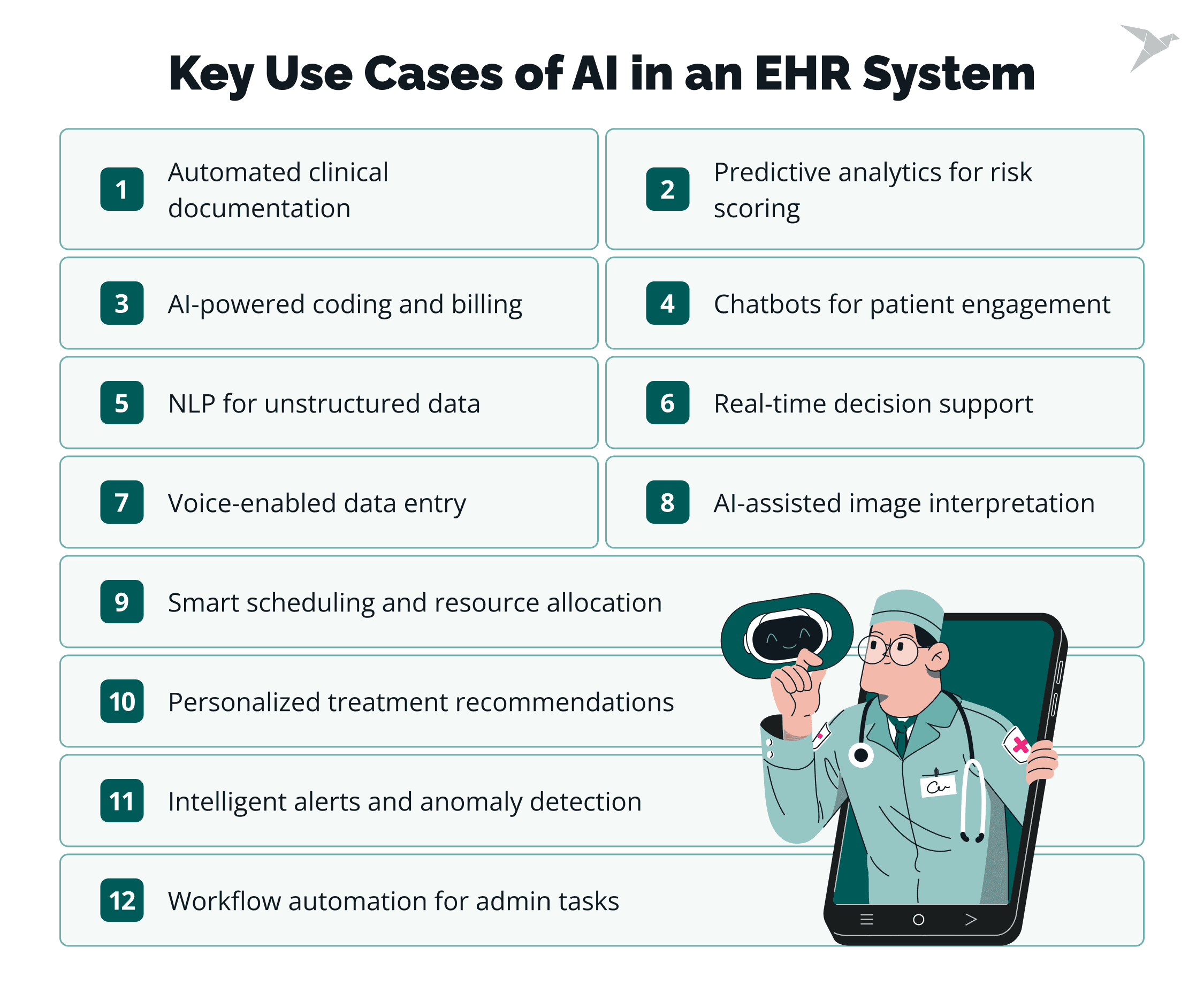
Automated clinical documentation and note generation
Nobody becomes a doctor because they love typing notes. With the right AI tools, your system can turn spoken words, short phrases, or structured inputs into full visit notes. It can pull in key info from past records, summarize what happened, and format it all cleanly so your team spends less time documenting and more time connecting with patients.
Predictive analytics for patient risk scoring
AI can help spot what humans might miss. It reviews patterns in a patient's medical history, lab results, or symptoms and flags who’s at risk before it becomes urgent. That means earlier action, more personalized care, and fewer readmissions down the line.
AI-powered medical coding and billing optimization
Billing mistakes cost time and money. AI helps you get it right the first time. It reads provider notes, suggests the right codes, and checks for errors before claims are sent. The result? Fewer denials, faster reimbursements, and a smoother handoff from care to payment.
Smart scheduling and resource allocation
AI can take the guesswork out of scheduling. It helps balance appointments based on provider availability, patient history, visit type, and even past no-show data. It can also flag gaps or overloads so your calendar works smarter, not harder.
Natural language processing (NLP) for unstructured data
Lots of valuable clinical info lives in free text like notes, referrals, or patient messages. NLP helps your EHR understand that mess of words and turn it into usable, comprehensive patient data. That means better search, cleaner records, and more insight without extra work.
Personalized treatment recommendations and care plans
AI doesn’t replace your medical team. It supports them. Based on real-time data and evidence-based guidelines, AI can suggest next steps, flag missing actions, or highlight best practices, giving clinicians a second set of eyes when it matters most.
Real-time clinical decision support
Think of this as a smarter alert system. AI watches what’s happening in the moment (like a new prescription or a lab result) and quietly checks it against rules, risks, and patient history. If something’s off, it says so. Not with 20 popups. Just the ones that count.
Voice-enabled data entry and navigation
Hands full? No problem. Voice tools let providers dictate notes, request lab results, or navigate patient records without typing. It saves time, cuts clicks, and makes your system feel less like a form and more like a tool that works with you.
Intelligent alerts and anomaly detection
AI can keep an eye on the system at all times. If vitals suddenly spike, if a diagnosis doesn’t fit the patient information, or if something just feels off, it can raise a flag. These quiet safety checks can prevent small issues from becoming big ones.
AI-assisted image and diagnostic interpretation
In fields like radiology or dermatology, AI can support the review process. It highlights patterns in scans, flags areas for closer look, and helps prioritize cases that need quick attention. It’s not a replacement for human review but it speeds it up.
Chatbots for patient engagement and support
Not every question needs a person to answer it. Smart chatbots can help patients schedule appointments, check their meds, fill out pre-visit forms, or get post-care instructions. That frees up your staff for the stuff that does need a human touch.
Workflow automation for administrative tasks
AI can quietly handle busywork. Matching scanned documents to the right record. Verifying insurance eligibility. Sorting incoming messages. It takes repetitive tasks off your team’s plate and keeps the work moving in the background.
Bottom line: AI won’t magically fix a clunky EHR. But when it’s built into the right places, it turns a good system into a great one.
If you’re wondering how to develop EHR sofware that works today and tomorrow, it’s worth thinking about where AI can give your team back time, focus, and confidence. And if you’re not sure where to start, we can help.
What Is Needed for an EHR system To Be HIPAA-Compliant
AI is the quiet helper in the background, doing the hard stuff so your team doesn’t have to. Used well, AI takes the pressure off healthcare professionals: doctors, nurses, and admin staff. It helps them focus more on people and less on paperwork, coding, or chasing lab results. And when you build a custom EHR system, you get to decide exactly where that help shows up.
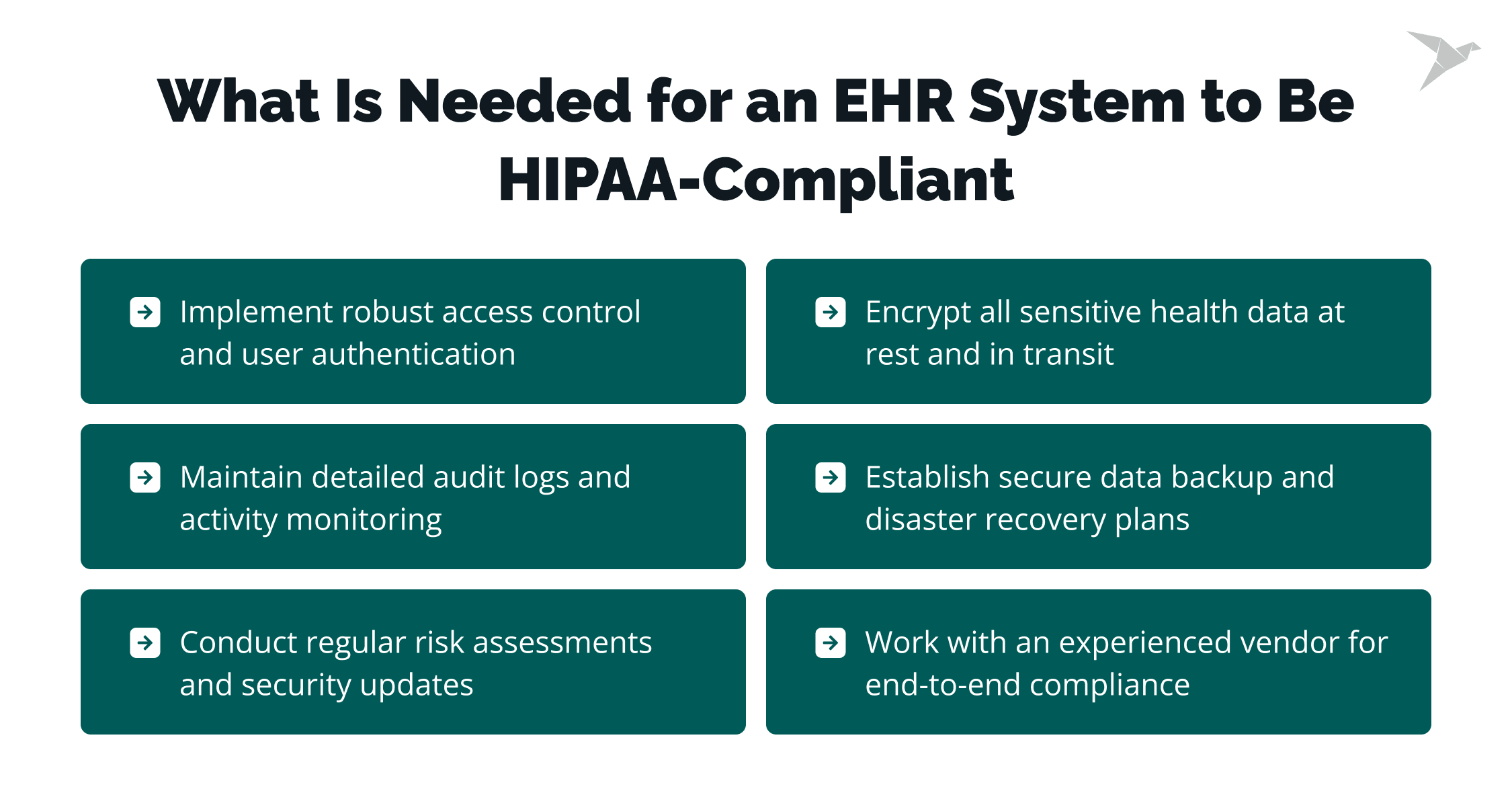
Implement robust access control and user authentication
You need to know exactly who’s accessing what and make sure no one sees more than they should. That means role-based access, secure logins, and multi-factor authentication. Each user should only see the data that’s relevant to their role. No more, no less.
Encrypt all sensitive health data at rest and in transit
HIPAA requires encryption. But more than that, it's just good practice. Every bit of data should be encrypted both while stored and when it’s being transferred. That protects against breaches, leaks, and unauthorized access.
Maintain detailed audit logs and activity monitoring
You need a clear trail of who did what and when. Audit logs keep track of every login, file access, change, and message. If something goes wrong or if there’s ever an investigation, these logs show exactly what happened and help you respond quickly.
Establish secure data backup and disaster recovery plans
Things break. Systems go down. But healthcare can’t afford to pause. Your EHR needs a backup plan. Literally. That includes regular data backups, secure storage, and a recovery strategy to get everything back online with minimal disruption.
Conduct regular risk assessments and security updates
Threats change fast. So should your defenses. A compliant EHR should include regular security reviews, penetration testing, and updates that patch vulnerabilities as they appear. HIPAA is a continuous process.
Work with an experienced vendor like TechMagic to ensure end-to-end compliance
HIPAA is complex, and missing just one detail can lead to major consequences. When you partner with a team that’s done this before, like us at TechMagic, you get a system that’s not just secure, but smartly built for long-term protection.
Ready to Build an EHR that Actually Works for You?
You don't need another rigid, slow-moving system that makes your team's job harder.
You need a platform that's built around your workflows, your goals, and your vision for better care.
At TechMagic, we've spent years building custom EHR solutions and other healthcare software for startups, clinics, hospitals, and digital health companies across the globe. Small private practices and enterprise-grade solutions like MHC's EMR platform. Our portfolio runs deep, and our team knows how to deliver.
Need to build from scratch? We've got you.
Want to move fast without sacrificing flexibility? We're also official partners of Medplum, an open-source FHIR platform that lets us build secure, compliant, and affordable EHR systems with speed and confidence.
Every project we take on is built around real collaboration.
No guesswork. No bloated timelines. Just smart, reliable systems made to fit how your team actually works.

Wrapping Up
A well-built EHR software helps people work better. It reduces friction, improves care, and gives healthcare teams room to breathe.
As the industry keeps moving toward smarter systems, connected care, and AI-supported decisions, your software needs to keep up. Fast.
That’s why building something custom = building the right ones, for the way your team actually works.
And that’s where TechMagic, an EMR/EHR software development company with 11+ years of experience, can help.
We know what it takes to build EHR systems that are flexible, secure, and made to scale. While delivering EHR software development services, we bring together strategy, design, development, and real-world healthcare experience to help you move fast and build robust EHR software solutions with confidence.
So if you’re thinking about how to build an EHR system that works today and grows with you tomorrow, we’re here when you’re ready.
Let’s make something that lasts.
FAQ
What is EHR software?
EHR (Electronic Health Record) software is a digital system that stores, manages, and shares patient health information across different healthcare providers. It helps streamline clinical workflows, improve care coordination, and support better decision-making.
What types of features are listed for EHR software?
Key features of an electronic health record system include a patient portal, appointment scheduling, clinical documentation, e-prescribing, billing, lab integration, role-based access, real-time data sync, telemedicine, and AI-powered decision support.
How much does it cost to build an EHR/EMR system?
Custom EHR system development can range from $30,000 to $500,000+, depending on complexity, integrations, and compliance needs of your electronic medical record system. Using platforms like Medplum can speed up delivery and reduce EHR/EMR system costs.
What are the three components of the EHR?
The three core components are clinical workflows + data management, administrative + billing functionality, and interoperability + integrations with labs, pharmacies, and external systems.


















 TechMagic Academy
TechMagic Academy