Hacking Apps for Compliance: Essential Guide to PCI DSS Penetration Testing
Last updated:17 October 2025

Every company that processes payments knows three letters that define how secure its systems really are: PCI. Yet few realize how much depends on one specific requirement called penetration testing.
The success of any app, regardless of industry or scale, depends on how well its systems withstand real-world threats and meet strict compliance standards. PCI DSS penetration testing sits at the core of every PCI audit, revealing how simulated attacks, ethical hackers, and controlled breaches expose vulnerabilities before criminals can exploit them.
We’ve noticed that many of our clients want clarity on what PCI DSS application penetration testing actually requires, who should perform it, and how to turn it from a checkbox into a true security value. Seeing this growing need, we’ve gathered our experience into one practical PCI DSS penetration testing guidance for app. Let’s break it down.
Key takeaways
- Pentesting is mandatory under PCI DSS, but its real value lies in proving that security controls work in practice.
- Tests must follow recognized methodologies (OWASP, NIST, PTES), cover all systems in the CDE, and include retesting after remediation.
- Web and mobile apps are often the most exposed parts of the cardholder data environment, so they must be PCI DSS compliant.
- Qualified, independent experts, preferably CREST-accredited, should conduct PCI pentests to ensure credible, audit-ready results.
- Real-world pentests uncover practical risks, such as IDOR vulnerabilities or authentication flaws, that directly map to PCI requirements.
- Continuous, AI-assisted testing is emerging as the new standard, especially for cloud and API environments.
- Human expertise and security awareness training remain irreplaceable for finding logic flaws and assessing real business impact.
- Organizations that integrate pentesting into regular operations achieve stronger security, smoother audits, and greater customer trust.
PCI DSS and The Role of Penetration Testing
PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) sets the baseline for how businesses protect cardholder data. If you store, process, or transmit payment information, it is mandatory. This standard defines how you prevent fraud and protect your customers.
Regular pentesting, including internal penetration testing and external vulnerability scans, is one of its core expectations and key requirements. It is a controlled, human-led simulation of real attacks that finds weaknesses before criminals do.
A professional penetration tester does more than surface issues from scanners; they provide insights that any site owner can use to improve their security posture. The goal of this security service is to prove impact, provide actionable fixes, and generate evidence auditors can trust. PCI also expects testing to be done by qualified, independent professionals (e.g., CREST-accredited teams), so results are unbiased and credible.
Watch a Short Video on Our Experience Testing Applications for PCI DSS Compliance
Why PCI DSS Requires Penetration Testing
Besides being one of the core PCI DSS requirements, pentesting is one of the most effective ways to verify that your security controls actually work. It turns compliance into tangible security assurance.
Under PCI DSS (Req. 11.x), tests are:
- Perform penetration testing at least annually and after significant changes to comply with PCI DSS Requirement 11.3.
- Cover both external and internal systems in the cardholder data environment (CDE).
- Segmentation testing is required annually for merchants and semi-annually for service providers to ensure controls are operational.
- And verify network segmentation if you use it.
Going deeper than compliance
We see penetration testing as a real-world stress test for your security controls. Security experts simulate genuine attack scenarios, using the same techniques as malicious actors. However, they do it in a safe and controlled way, often within a virtual machine environment to replicate production safely.
Automated vulnerability scans may produce lists of issues. A manual pentest, on the other hand, goes deeper and focuses on which vulnerabilities are exploitable in practice, what business impact they could have, and how to prioritize and fix them effectively.
For example, testers may execute a SQL command injection or privilege escalation to validate system resilience against online attacks. This approach validates that your:
- Firewalls, authentication systems, and encryption perform as intended.
- Internal and external networks are properly segmented and secure.
- Recent updates or changes haven’t introduced new risks.
- Defenses have been independently verified and documented for auditors.
Ultimately, PCI DSS includes penetration testing because it provides something no automated process can: evidence that your systems are truly secure. It strengthens trust, reduces exposure, and validates that your defenses can withstand real attackers.
Penetration testing vs. vulnerability scanning
While vulnerability scanning automatically identifies known weaknesses, penetration testing goes further. It actively exploits vulnerabilities to reveal how deep an attacker could go.
Within PCI DSS assessments, these two activities complement each other: scanning provides continuous visibility into security gaps, while pentesting validates how effectively your defenses hold under real-world attack scenarios.
AI now strengthens both sides of this process. Automated scanners use machine learning to prioritize findings and reduce false positives, while AI-assisted pentesting helps simulate sophisticated, adaptive attack patterns. This synergy allows organizations to assess their true resilience against emerging threats faster and more accurately.

Check our

Application Penetration Testing for PCI DSS
Applications are often the most exposed and frequently targeted part of the cardholder data environment. Every login form, payment gateway, or API endpoint can become an entry point for attackers if not properly tested. That’s why PCI DSS places strong emphasis on application penetration testing – to ensure your apps are actually secure.
How does it work in general?
A penetration test consists of three stages: pre-engagement, engagement, and post-engagement. A PCI app pentesting examines how your web and mobile apps handle data, sessions, and authentication under real-world attack conditions (pre-engagement).
Testers simulate cyberattacks to uncover vulnerabilities such as injection flaws, cross-site scripting, broken access control, insecure session handling, misconfigurations, and outdated components (engagement). The last stage is retest and remediation report (post-engagement).
PCI penetration testing for app is guided by the OWASP Top 10 framework and PCI DSS secure coding requirements, so that findings align with industry-recognized best practices. The last one verifies that your app:
- encrypts stored data;
- secures transmission over public networks;
- protects sensitive workflows like checkout or account management.
Each of our test results in a detailed report that includes verified findings, their impact, and clear remediation guidance. Once fixes are implemented, we perform a follow-up retest to confirm that vulnerabilities are resolved, which will be detailed in the penetration test report .
The final documentation we provide serves as evidence during PCI audits, proving that your applications have been independently tested and validated for security.

Pentesting and changes in PCI DSS 4.0
The latest version of the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard, PCI DSS 4.0, marks a major shift in how organizations must validate and maintain security, especially around penetration testing.
The PCI SSC (Security Standards Council) now encourages many organizations to adopt continuous testing practices and align their programs with global audit expectations.
Firstly, the update introduced a three-year transition period that began on March 31, 2022, giving organizations time to adapt to the new framework. From March 31, 2025, all requirements, including updated pentesting controls, are fully mandatory.
Under PCI DSS 4.0, penetration testing remains a core expectation but with added emphasis on continuous validation, segmentation testing, and documented remediation. The goal is to ensure that security controls around the cardholder data environment are tested regularly and proven effective.
Compliance is enforced by major credit card brands: Visa, Mastercard, American Express, Discover, and JCB. It also applies to all merchants and service providers that store, process, or transmit payment card data.
AI in modern applications
As apps adopt AI features like chatbots or fraud-detection models, new risks appear: data leakage, model manipulation, etc. PCI application pentests now also assess these AI components to ensure they don’t expose cardholder data, while using AI tools themselves to simulate more adaptive attack scenarios.
Types of PCI DSS Penetration Testing
As previously mentioned, PCI DSS requires penetration testing across every layer of the cardholder data environment to ensure that no weak points are left unchecked. This can include several types of tests depending on how your systems are built. Each of these PCI app penetration testing types includes a different attack surface. Let’s take a closer look at them.
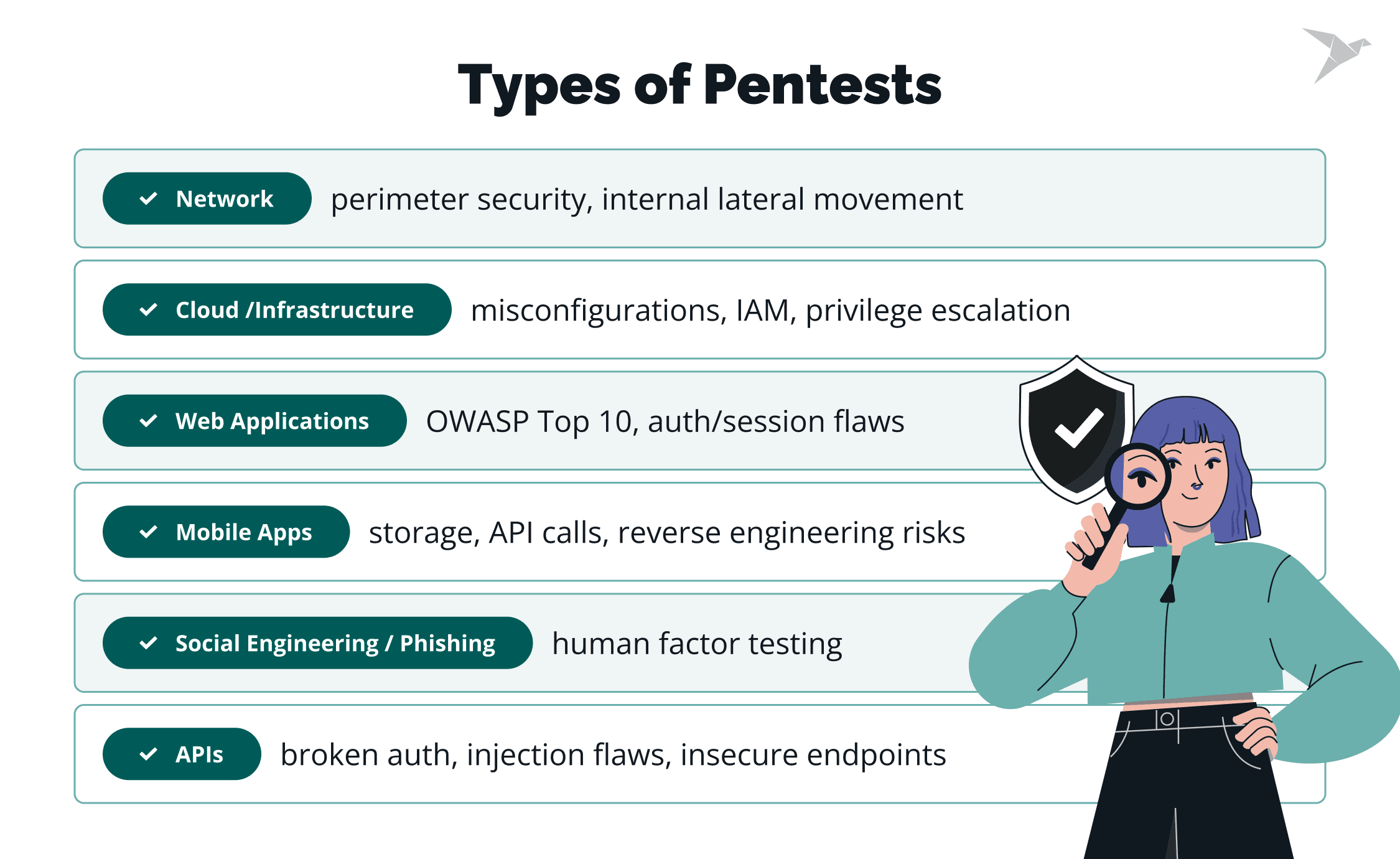
External network testing
This type of pentesting simulates real-world attacks from outside your organization. The goal is to identify vulnerabilities in internet-facing systems that could expose cardholder data to unauthorized users. It covers firewalls, web servers, APIs, etc.
Internal network testing
Internal PCI DSS penetration testing for app focuses on what happens if an attacker or insider gains access to the internal network. These tests look for misconfigurations, privilege escalation paths, and lateral movement opportunities that could compromise sensitive systems.
Web application testing
Web apps often handle payments directly, making them a core part of the PCI DSS scope. Pentesters assess authentication flows, session management, input validation, and business logic. All of this to detect issues such as injection flaws, broken access control, and insecure configurations (many mapped to the OWASP Top 10).
Mobile application testing
Mobile apps process sensitive payment data and connect directly to backend APIs. Testing focuses on local data storage, API communication, reverse engineering, and weak authentication mechanisms that could expose user or cardholder information.
Cloud and infrastructure testing
PCI DSS expects regular validation of access controls, IAM roles, and configurations for organizations running workloads in the cloud. This type of pentesting identifies privilege escalation paths, exposed services, and misconfigured storage that could lead to data leakage.
Social engineering (recommended)
Social engineering tests aim to identify risks arising from users' inability to recognize malicious requests.
It is not mandatory. However, testing your human layer through phishing simulations or security awareness checks helps ensure employees recognize and resist real-world attacks that could compromise PCI systems.
Together, these testing types give a complete view of your environment’s security posture. When covering both internal and external perspectives, PCI DSS ensures that all systems handling, storing, or transmitting cardholder data are protected against real threats.
PCI DSS Penetration Testing Methodology and Scope
In 99% of cases, the PCI DSS penetration testing guidance follows clear, verifiable steps that align with industry standards and audit expectations.
1. Recognized methodologies
Tests must follow accepted frameworks such as OWASP, NIST SP 800-115, or PTES. These define how to plan, conduct, and report pentests using realistic attack scenarios while maintaining control and consistency. Three main methods of pen tests are black-box, white-box, and grey-box.
2. Scope definition and verification
Good practice is to include all systems and applications that store, process, or transmit cardholder data, plus any connected components that could impact the CDE. If network segmentation reduces scope, pen testers must validate segmentation effectiveness to ensure isolation holds in practice.
3. Required frequency
Pentests are required at least once a year and after significant system or application changes. Large or high-risk environments often test more frequently to keep security evidence current.
4. Remediation and retesting, pentest report
PCI DSS emphasizes that pentesting is a part of an ongoing improvement cycle. Once vulnerabilities are fixed, the environment should be retested to verify remediation and update documentation.
The final report and retest evidence serve as proof for auditors that security issues were fully resolved. Documentation and mapping of all systems handling cardholder data, along with maintaining an up-to-date inventory, is essential for PCI DSS compliance.
Penetration testing of a cloud-native hospital management system before the annual ISO 27001 audit
Who Should Perform PCI Pentests
Not everyone can perform a PCI-compliant pen test. PCI app penetration testing requirements need pentesters to be third-party professionals, accredited with certifications, or part of an approved company, such as a CREST-accredited provider. The process of pentesting involves setting clear rules of engagement to establish boundaries and expectations.
CREST certification is widely recognized in the industry as a mark of competence. It proves that a tester has demonstrated advanced technical skills, follows standardized methodologies, and adheres to strict ethical and procedural standards.
CREST-accredited pentesting provider ensures your tests align with PCI DSS expectations, produce verifiable evidence for auditors, and deliver reliable, actionable insights. It also reassures customers and partners that your organization’s security assessments meet globally recognized quality standards.
So, in other words, these must be people who aren’t involved in developing or managing the systems they assess, ensuring that performed triggered assessments are unbiased. And the PCI Security Standards Council recommends working with qualified pentesting providers who have relevant certifications. This way, the findings are unbiased, and the results withstand audit scrutiny.
Our Cases on PCI Penetration Testing
We’ve worked with clients of different scales and industries. But in this article, we’ll share two particular cases of apps’ pentesting for PCI: web and mobile.
Web app case: Predictable voucher IDs (IDOR)
During a PCI DSS pentest for an e-commerce platform, our penetration testing team discovered that the “share a voucher” feature used short, sequential voucher IDs in URLs. Without authentication, attackers could easily enumerate IDs and access other users’ data, like emails, order references, and even partial personal details.
Our remediation measures
- Replaced predictable IDs with unguessable, high-entropy tokens.
- Enforced token validation and authentication checks.
- Minimized response data to exclude unnecessary or sensitive fields.
- Added rate limiting, monitoring, and alerting for suspicious activity.
Outcomes
Thanks to the pentest, the client’s team addressed critical gaps and achieved full compliance with PCI DSS requirements 3–4 (data protection), 6.5–6.6 (secure coding), 8 (authentication), 10 (logging), and 11.3–11.4 (testing and retesting).
In practice, this meant stronger data encryption, secure handling of payment information, improved authentication flows, and consistent activity logging across systems. The retest confirmed that no unauthorized access was possible and provided complete audit evidence for certification.
Mobile app case: Token issued before OTP
In a mobile banking app under PCI DSS scope, we identified a critical flaw in the authentication flow. Before OTP verification, the backend issued a JWT token after password entry and accepted it for sensitive account APIs. Combined with weak rate limiting, this allowed attackers to bypass two-factor authentication entirely.
Our remediation measures
- Issued access tokens only after OTP verification.
- Restricted temporary tokens with proper scoping.
- Encrypted local storage via platform keystores and keychains.
- Removed sensitive data from logs.
- Strengthened rate limiting and anomaly detection.
- Conducted a full retest to verify all fixes.
Outcomes
These improvements brought the system into full alignment with PCI DSS controls: Req. 3–4 (data protection), 6.5–6.6 (secure coding), 8 (strong access control), 10 (logging), and 11.3–11.4 (testing and retesting).
In practice, this meant stronger encryption of stored and transmitted data, secure coding standards applied across the codebase, tighter authentication policies, and comprehensive activity logging. The follow-up testing confirmed all issues were resolved, no unauthorized access was possible, and the evidence package met auditor requirements.
The outcome: verified compliance, improved system resilience, and greater confidence in the organization’s overall security posture.
As you can see in both cases, PCI-focused pentesting exposes not just technical misconfigurations, but real-world business logic flaws. At the end of the day, it helps turn compliance testing into measurable, lasting security improvements.
The Value Behind PCI DSS Pentests
While PCI DSS requires regular pentesting, the greatest benefit comes when it becomes part of an organization’s ongoing security strategy.
This is one of the most effective ways to validate and strengthen PCI DSS compliance. One of the PCI DSS penetration testing requirements for app is that it must be performed by an external certified expert (CREST-certified would be the best option), or coordinated by a qualified internal resource when allowed by scope.
Strengthening security over time
Each pentest reveals exploitable weaknesses that automated tools overlook. Acting on those findings helps teams fix real issues, strengthen controls, and improve detection and response before attackers can exploit them. Over time, this process builds measurable resilience rather than short-term audit readiness.
Recent data shows how much security testing contributes to real protection.
- BreachLock’s 2024 report revealed a 150% increase in critical web vulnerabilities year over year.
- The 2024 Fortra Pen Testing Report found that 82% of organizations use pentesting to prioritize risk, and 72% say it has prevented at least one breach.
Building confidence and trust
Independent, third-party testing demonstrates that your defenses have been verified. Regular PCI-focused pentests show customers, partners, and auditors that your security program operates continuously instead of during audit season. This consistency builds trust and differentiates your organization in industries where data protection drives reputation.
Simplifying audits
When pentesting is built into everyday workflows, audits become faster and more predictable. Most findings are already addressed throughout the year, leaving annual PCI reviews focused on validation, not crisis management.

Wrapping Up: Future of Pentests for PCI
Many teams move to a continuous testing model. It consists of lightweight, recurring checks with expert support (security-as-a-service). This helps developers, QA, and ops teams build secure habits, keep evidence fresh, and stay resilient between audits.
Human expertise remains essential
Despite automation and AI, experienced pentesters will stay critical to PCI security. Manual testing remains the only way to uncover business logic flaws, authentication weaknesses, and misconfigurations that automated tools overlook. The future belongs to teams that combine intelligent automation with deep human expertise.
AI-driven testing becomes standard
Artificial Intelligence is transforming both offensive and defensive security. Attackers use it to automate payloads and adapt exploits in real time. Ethical hackers respond by integrating AI-driven analysis into pentesting, accelerating discovery, and identifying complex vulnerabilities that traditional tools might miss.
Continuous testing replaces annual cycles
Annual or post-change pentests will no longer be enough. PCI programs are moving toward continuous validation, where testing runs throughout the year. Automated scanning, combined with expert manual reviews, helps maintain a consistent security baseline and keeps PCI evidence up to date.
Cloud and API testing take the lead
As payments shift toward cloud-native systems, APIs, and microservices, PCI DSS pentests will increasingly target these environments. IAM policies verification, encryption, and third-party integrations will become central to protecting cardholder data in distributed architectures.
Automated evidence for auditors
Modern pentesting platforms now produce audit-ready documentation that maps findings directly to PCI DSS controls. This automation makes it easier to demonstrate compliance while reducing manual reporting effort and preparation time.
In short, PCI pentesting is moving toward a model of continuous, intelligent assurance that reflects the updated standard. This is one that balances speed, automation, and expert insight to keep pace with modern threats and evolving compliance demands.

FAQ
How often must penetration testing be performed for PCI DSS compliance?
PCI DSS requires penetration testing to be performed at least annually and after any significant changes to the environment or systems that could impact security.
What systems are in scope for PCI pentesting?
The scope includes all systems that store, process, or transmit payment card information, as well as any connected networks and systems that could impact the security of the cardholder data environment. Segmentation controls must also be tested if used.
What is the difference between penetration testing and vulnerability scanning?
Vulnerability scans are automated tools that detect potential vulnerabilities, while a penetration test is a manual, in-depth process where testers actively attempt to exploit vulnerabilities to assess real-world risks. Regular vulnerability scans are required at least quarterly and are separate from penetration testing.
What should a PCI pen test report include?
The report must document all vulnerabilities found, their severity, evidence or proof of concept, the scope and methodology of the test, and details on segmentation testing if applicable. It is critical for maintaining PCI DSS compliance.
What changes does PCI DSS v4.0 introduce regarding penetration testing?
PCI DSS v4.0 expands requirements to include remediation of both exploitable vulnerabilities and security weaknesses, mandates testing of all internal and external systems affecting the CDE, and requires penetration testing to be regularly performed with updated methodologies.
Can penetration testing help prevent data breaches?
Yes, by identifying and addressing exploitable vulnerabilities and security weaknesses before attackers can exploit them, penetration testing strengthens your security posture and reduces the risk of data breaches.

 Software Development
Software Development Security Services
Security Services Cloud Services
Cloud Services Other Services
Other Services















 TechMagic Academy
TechMagic Academy