Guide for AWS Microservices: What Is it, Architecture, Use Cases & More

Director of Cloud and Cybersecurity, AWS Expert, big fan of SRE. Helps teams to improve system reliability, optimise testing efforts, speed up release cycles & build confidence in product quality.

Eager to learn more about AWS microservices use cases, architecture, and scaling? Here’s an in-depth look at the microservices impact on app development.
Although microservices have been around for a long time, they gradually gain more popularity within deployed systems. Such web giants as Amazon, Twitter, Netflix, and PayPal have already adopted the AWS microservices architecture. Following their successful example, many companies also decided to move in the same direction — they gradually move away from the rough monolith to an easier and more flexible microservice-based architecture.
But what is special about AWS microservices? Is there any business value? What is the most effective AWS microservices example? Here’s an in-depth look at the microservices impact on web app development, the main benefits, and most popular Amazon microservices use cases.
What Are AWS Microservices?

Let’s begin this tutorial with the basics. Microservices are independent pieces of software that run separately from each other and deliver certain functions. Communication between them happens over defined APIs. This means that programmers can use different development tools for every function and aren’t limited by only one programming language.
On the plus side, each microservice can be developed and scaled separately, which drastically improves programmers’ performance. What’s more, it also increases the cost-effectiveness and simplicity of infrastructure management compared to a conventional monolithic app. In other words, it’s a service-oriented architecture — a simple method of building apps, broken down into independent service units.Why choose AWS microservices? The thing is that AWS (Amazon Web Services) is the best solution for building a microservice-based application because this cloud platform offers a plethora of PaaS, IaaS, and SaaS solutions. It also provides a variety of SDK packages and building blocks to support software of any scale.
Benefits of microservices on AWS

We’ve just covered the basics, so now is the time to move on to discussing the key benefits of microservices on AWS:
- Scalability — one component of the app can be scaled separately;
- Quicker to deploy — the deployment of certain app components doesn’t influence other services;
- Programmers don’t depend on each other — dev teams that work on building one app component can be more productive;
- Easier to understand — as one component of the app doesn’t depend on others, it is simpler for programmers to follow microservices code;
- Lifecycle Automation — separate components are simpler to control in a CI/CD environment;
- Reusability — one app component can be easily reused by other apps;
- More independence for developers — they can work autonomously and make technical decisions faster.
Cases of AWS Microservices Use
Let’s review the most popular Amazon microservices use cases:

Machine learning
The main distinctive feature of a machine learning environment is that it can easily collect and analyze informational flow. The overriding purpose of the machine learning framework is to calculate the result. When the data is used in an ML environment, it goes through a few steps before the final result is reached. The main advantage of using microservices is the capability to apply many ML models to the same data in order to get a more precise result.
Extensive data pipelines
When analyzing AWS microservices consulting use cases, we couldn’t pass this one by. To explain this use case, let’s provide some examples. Let it be a simple reporting system used to control sales in retail shops. In such a scenario, absolutely each step related to data preparation can be controlled by a microservice. We mean such simple operations as the collection of data flow, aggregation, enrichment, etc. The thing is that it is easy to trace the microservices workflow. Therefore, it takes less time and effort to find which microservice must be updated.
CPU or RAM Intensive Application Components
If necessary, one can spawn various instances of a CPU microservice without influencing the rest of the CPU power. Besides, there are also some difficulties related to the use of text analysis tools. The thing is that they take up a lot of space, and sometimes, it is really hard to redeploy them. Therefore, it would be more effective to separate them.
Scaling in AWS Microservices
Although AWS microservices have numerous benefits, scaling in AWS microservices is still a challenge for programmers.
In a conventional monolithic app, scaling is usually done by running a few copies of the app on servers. When it comes to a microservices environment, scaling is performed by scaling separate components. However, this task is quite challenging.
The thing is that microservices usually communicate with other services and are built in various code bases. Sometimes, they can be placed on different platforms. In this case, the use of an application delivery controller or proxy might be the right solution. This allows developers to find performance issues and speed up the scaling.
Working Principle of the Microservices Architecture on AWS
Programmers usually build apps with a few layers, where one layer is meant for user interface, the second — for business, and the third — for persistence. The main goal of an Amazon microservices architecture is to subdivide the software by functionality, which guarantees that absolutely each component is responsible for performing a certain function.
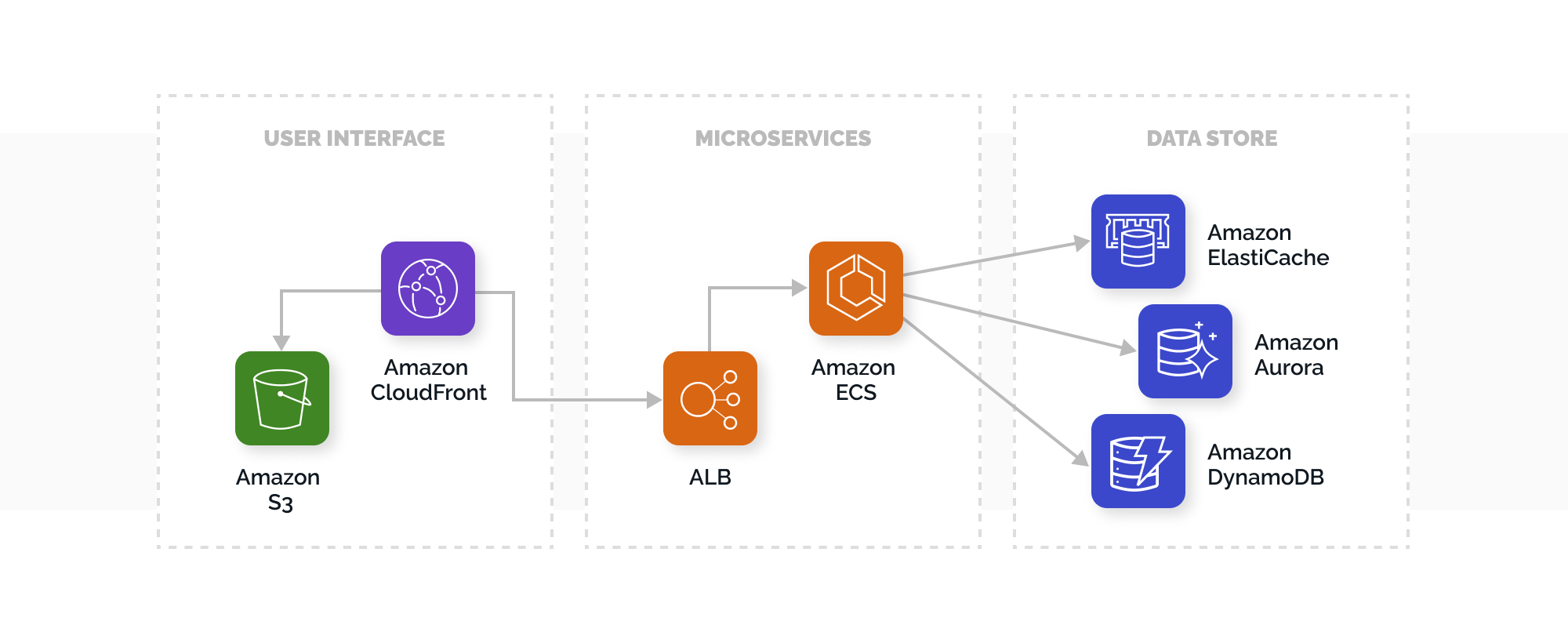
Let’s take a closer look at the main stages of app development using microservices:
- User Interface
The JavaScript framework is mostly used for building web apps. They are developed as single-page apps, communicating via REST or RESTful APIs. AWS suggests using Amazon CloudFront and S3 for hosting static web content.
- Microservices
AWS offers powerful building blocks to make microservices development easier. The most widely used approaches are microservices AWS Lambda, AWS Fargate, and Enterprise Kubernetes (used for running Kubernetes clusters on AWS).
With AWS Lambda microservices, developers can load code, check performance, and adapt the app to real demands. Lambda can be used with many programming languages.
Fargate (a well-known container management service from AWS) performs one goal — run serverless containers. Besides, with this tool, there’s no need to scale a cluster.
- Data storage
In this case, relational databases are used to store formatted data for microservices. Mostly, microservices apps are based on AWS database services, including Oracle, Amazon’s RDS, MySQL, PostgreSQL.
Let’s review the main functions performed by AWS microservices:

Compute
The thing is that the AWS service portfolio includes a broad selection of building blocks that can be integrated separately and enhance the app’s performance.
AWS Lambda allows programmers to run code without provisioning servers, which is one of the main use cases for AWS Lambda. One needs to upload code, and Lambda will be responsible for running and scaling. For example, when a website with no visitors is hosted on Lambda, there’s no need to pay for hosting. If a startup has a limited budget, it’s a good option to try.
Amazon Elastic Container Service is a powerful, scalable, and multi-featured management system that allows AWS clients to run apps in Docker containers.
Storage and Databases
Let’s take a closer look at the most popular solutions:
- Amazon Aurora (a powerful AWS database engine);
- Amazon DynamoDB (a well-known and reliable AWS NoSQL database);
- Amazon RDS (a tool that allows creating, controlling, and scaling a database);
- Amazon ElastiCache (improves the performance of microservices).
Networking
- Amazon Route 53 (a scalable and robust DNS service from Amazon);
- AWS App Mesh (guarantees communication between microservices; with this tool, it is easier to keep track of microservices that are running on AWS);
- Amazon API Gateway (improves the app performance by processing numerous API calls).
Interested to learn more about our AWS expertise?
Learn moreMonitoring and logging
- Amazon CloudWatch (mainly used for resource monitoring by collecting the main monitoring metrics);
- CloudTrail (makes security auditing easier).
Messaging
- Amazon SQS (a reliable message queue service that guarantees the scaling and decoupling microservices);
- Amazon SNS (used for pushing messages to subscribers).
DevOps
- AWS Developer Tools (a combination of services that allows software dev teams to be more efficient and build software quicker);
- ECR or Elastic Container Registry (Docker container image repository, responsible for the storage and deployment of containers).
Final Thoughts
As we can see, AWS microservices are a superb solution for developing, running, and updating powerful and scalable apps. AWS comes with a broad selection of robust building blocks used for handling microservices implementation.If you are currently looking for a trusted and time-proved development team with ample experience developing and managing microservice-based apps, don’t hesitate to contact TechMagic — your reliable partner with many years of experience in JavaScript development, AWS Serverless consulting, and native mobile app development. We follow the best practices and build reliable and scalable apps for our customers.



 Software Development
Software Development
 Security Services
Security Services
 Cloud Services
Cloud Services
 Other Services
Other Services
















 TechMagic Academy
TechMagic Academy
 linkedin
linkedin
 facebook
facebook
 twitter
twitter






















